2026
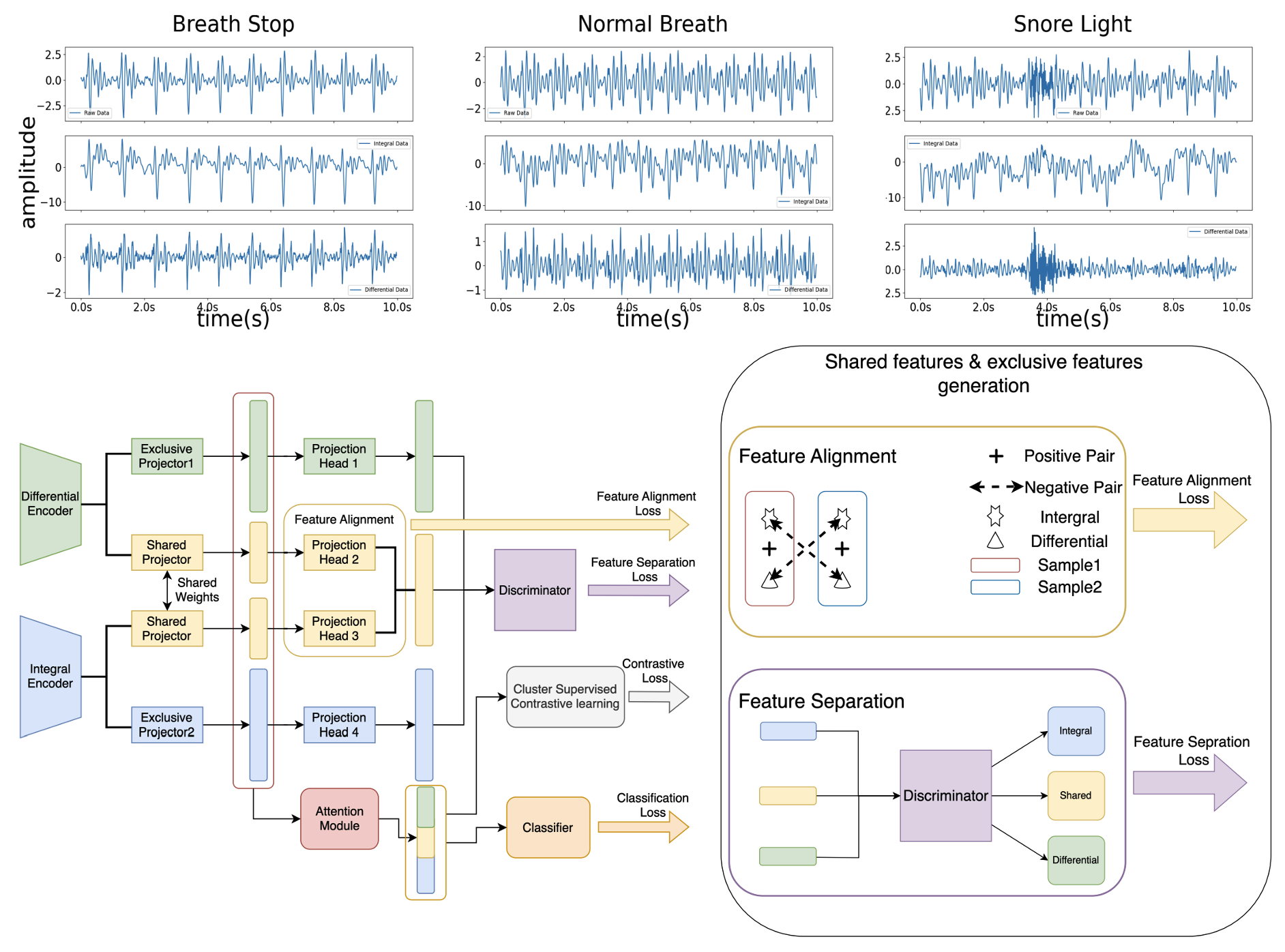
Attention Feature Fusion with Cluster Contrastive Learning for Snoring and Breath-Holding Detection Using Seismic Sensing
Yingjian Song, Jiayu Chen, Zixuan Zeng, Yida Zhang, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, Xiang Zhang, Fei Dou, Wenzhan Song
In 2026 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom) 2026
This paper proposes a contactless, engagement-free seismic-sensing system to detect snoring and breath-stopping for sleep apnea, avoiding the discomfort of wearables and the placement sensitivity of smartphone approaches. It introduces Attention Feature Fusion and Cluster Contrastive Learning, which uses differential/integral signal transforms plus attention-based feature fusion and supervised contrastive learning to separate snoring, breath-stopping, and normal breathing.
Attention Feature Fusion with Cluster Contrastive Learning for Snoring and Breath-Holding Detection Using Seismic Sensing
Yingjian Song, Jiayu Chen, Zixuan Zeng, Yida Zhang, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, Xiang Zhang, Fei Dou, Wenzhan Song
In 2026 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom) 2026
This paper proposes a contactless, engagement-free seismic-sensing system to detect snoring and breath-stopping for sleep apnea, avoiding the discomfort of wearables and the placement sensitivity of smartphone approaches. It introduces Attention Feature Fusion and Cluster Contrastive Learning, which uses differential/integral signal transforms plus attention-based feature fusion and supervised contrastive learning to separate snoring, breath-stopping, and normal breathing.
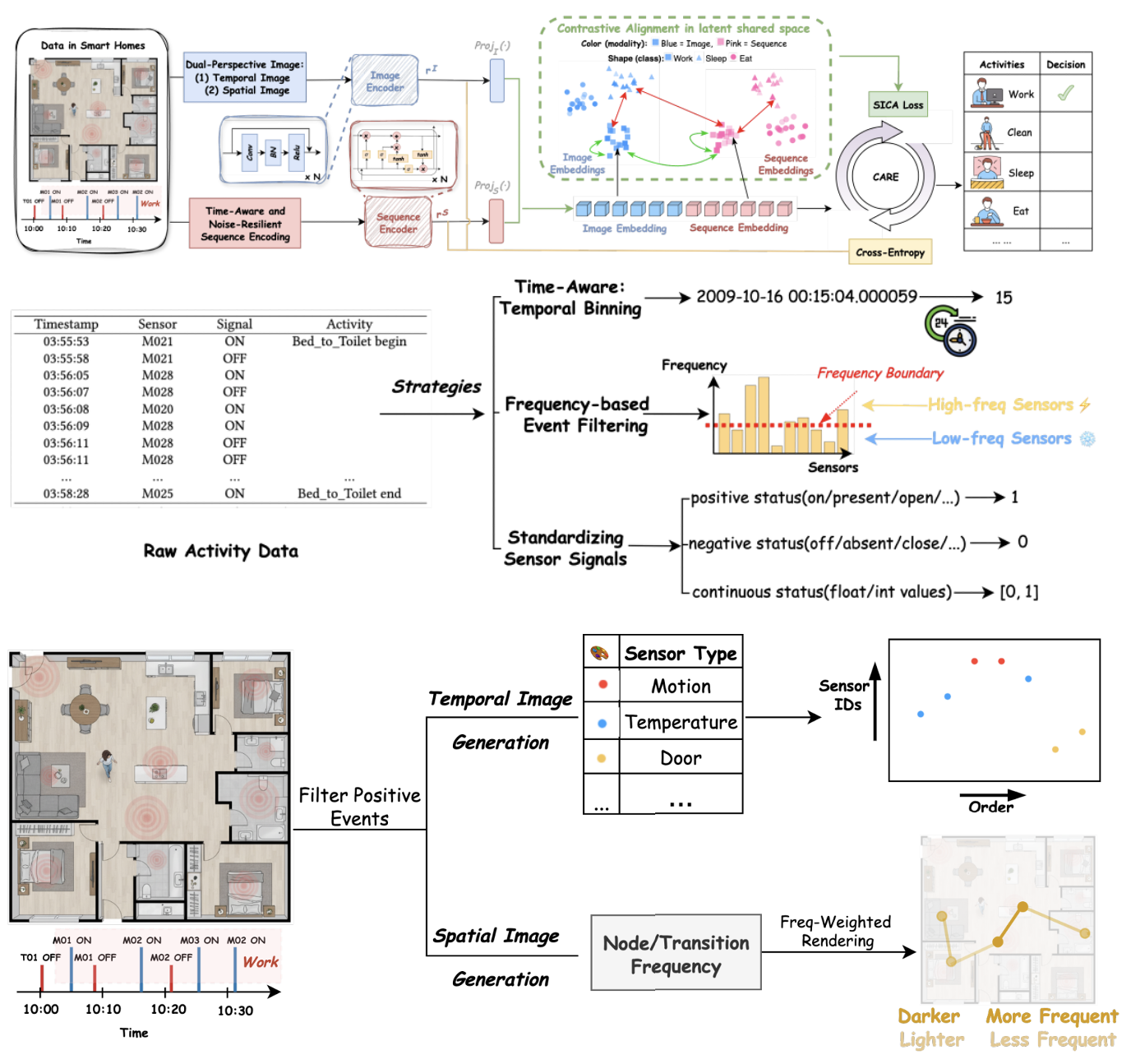
CARE: Contrastive Alignment for ADL Recognition from Event-Triggered Sensor Streams
Junhao Zhao, Zishuai Liu, Ruili Fang, Jin Lu, Linghan Zhang, Fei Dou
In 2026 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom) 2026
This paper presents CARE, an end-to-end framework for recognizing ADLs from event-triggered ambient sensors by aligning complementary sequence and image representations. Unlike sequence-only methods that lack spatial awareness and are noise-sensitive, or image-only methods that blur temporal dynamics and distort layouts, CARE enforces Sequence-Image Contrastive Alignment (SICA) while jointly optimizing classification with a contrastive-plus-cross-entropy objective. By combining time-aware, noise-resilient sequence encoding with spatially informed, frequency-sensitive image features, CARE learns aligned and discriminative embeddings.
CARE: Contrastive Alignment for ADL Recognition from Event-Triggered Sensor Streams
Junhao Zhao, Zishuai Liu, Ruili Fang, Jin Lu, Linghan Zhang, Fei Dou
In 2026 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom) 2026
This paper presents CARE, an end-to-end framework for recognizing ADLs from event-triggered ambient sensors by aligning complementary sequence and image representations. Unlike sequence-only methods that lack spatial awareness and are noise-sensitive, or image-only methods that blur temporal dynamics and distort layouts, CARE enforces Sequence-Image Contrastive Alignment (SICA) while jointly optimizing classification with a contrastive-plus-cross-entropy objective. By combining time-aware, noise-resilient sequence encoding with spatially informed, frequency-sensitive image features, CARE learns aligned and discriminative embeddings.
2025
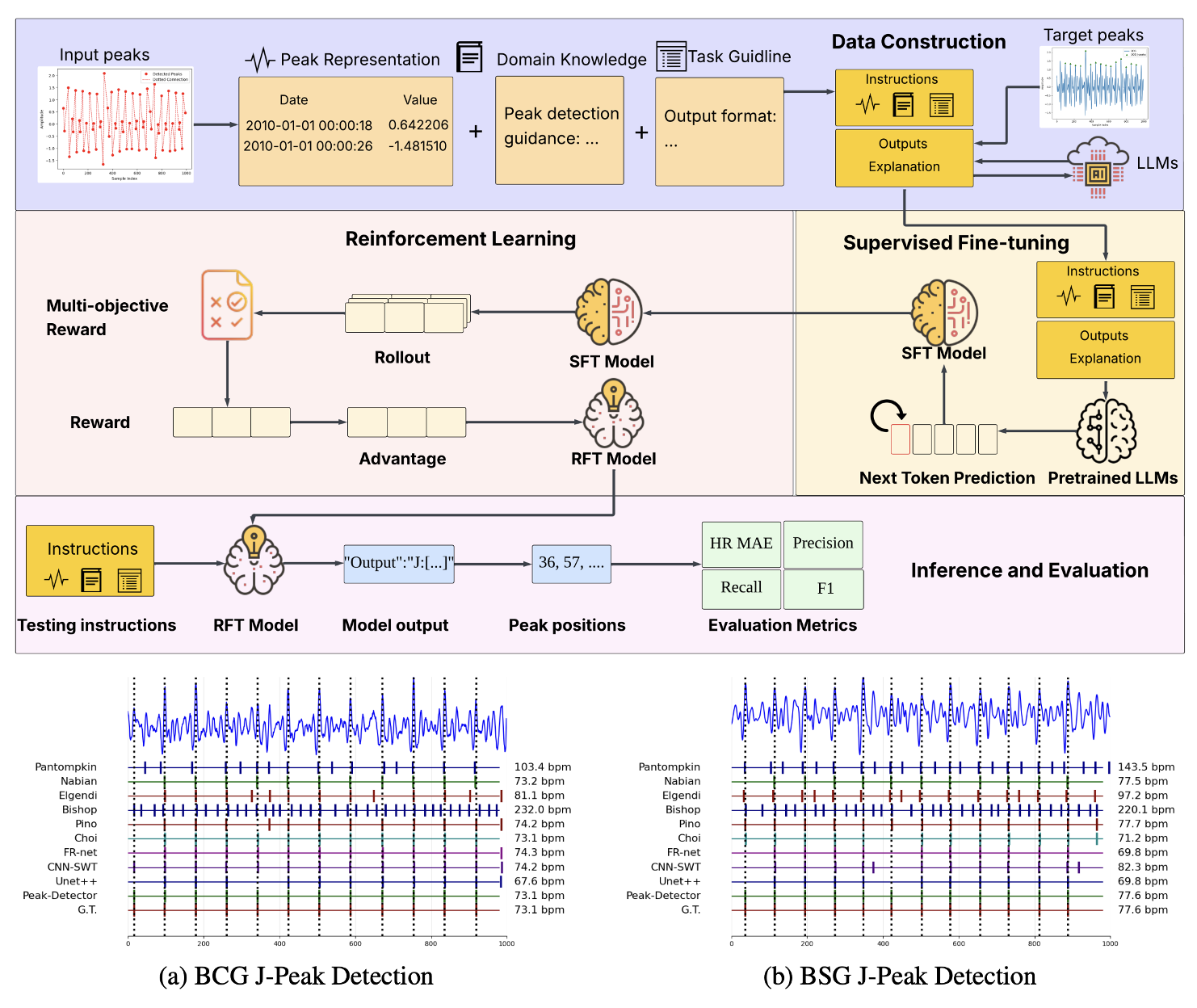
Peak-R1: Instruction-Tuned Large Language Models for Robust J-Peak Detection in Cardiomechanical Signals
Jiahui Li, Yida Zhang, Zixuan Zeng, Jiayu Chen, Xiang Zhang, Jin Lu, WenZhan Song, Fei Dou
Learning from Time Series for Health (TS4H @ NeurIPS 2025) 2025
This paper presents Peak-R1, an instruction-tuned LLM framework for robust, cross-modal, and explainable peak detection in cardiac-mechanical signals (BCG/BSG). Peak-R1 introduces a peak-representation that compresses time series while preserving salient events, enabling the model to reason over physiologically meaningful structure rather than noisy raw signals. Trained via supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning with a multi-objective reward, and augmented with a Peak-Explanation dataset, Peak-R1 achieves best or tied-best performance and provides rationales that expose failure modes and support human-in-the-loop annotation.
Peak-R1: Instruction-Tuned Large Language Models for Robust J-Peak Detection in Cardiomechanical Signals
Jiahui Li, Yida Zhang, Zixuan Zeng, Jiayu Chen, Xiang Zhang, Jin Lu, WenZhan Song, Fei Dou
Learning from Time Series for Health (TS4H @ NeurIPS 2025) 2025
This paper presents Peak-R1, an instruction-tuned LLM framework for robust, cross-modal, and explainable peak detection in cardiac-mechanical signals (BCG/BSG). Peak-R1 introduces a peak-representation that compresses time series while preserving salient events, enabling the model to reason over physiologically meaningful structure rather than noisy raw signals. Trained via supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning with a multi-objective reward, and augmented with a Peak-Explanation dataset, Peak-R1 achieves best or tied-best performance and provides rationales that expose failure modes and support human-in-the-loop annotation.
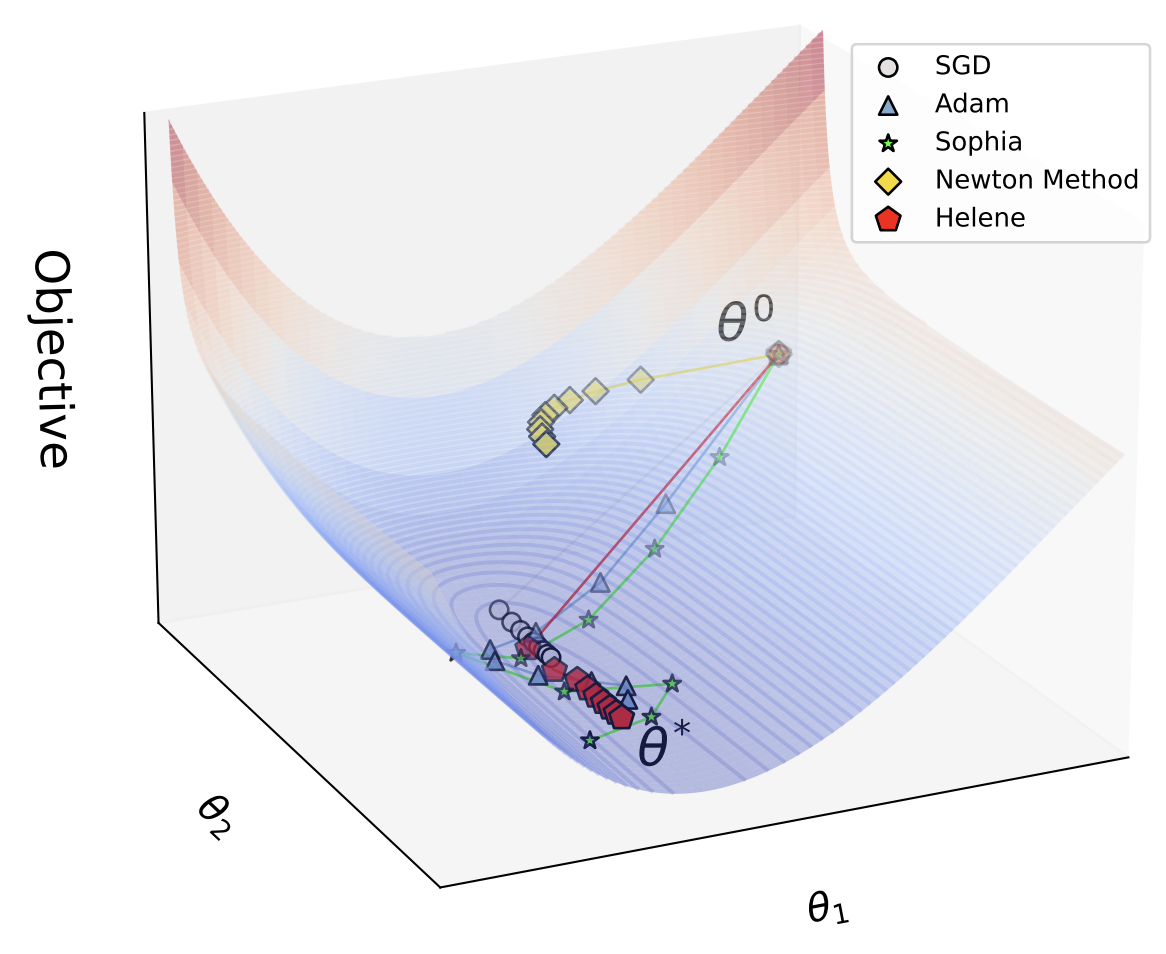
HELENE: Hessian Layer-wise Clipping and Gradient Annealing for Accelerating Fine-tuning LLM with Zeroth-order Optimization
Huaqin Zhao*, Jiaxi Li*, Yi Pan, Shizhe Liang, Xiaofeng Yang, Wei Liu, Xiang Li, Fei Dou, Tianming Liu, Jin Lu (* equal contribution)
Proceedings of the 2025 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025
This paper presents HELENE, a memory-efficient and scalable optimizer for fine-tuning large language models, addressing the slow convergence of zeroth-order methods like MeZO by incorporating annealed A-GNB gradients, diagonal Hessian estimation, and layer-wise clipping. HELENE achieves faster, more stable convergence with up to 20× speedup and improved accuracy, and it supports both full and parameter-efficient fine-tuning across large-scale models and tasks.
HELENE: Hessian Layer-wise Clipping and Gradient Annealing for Accelerating Fine-tuning LLM with Zeroth-order Optimization
Huaqin Zhao*, Jiaxi Li*, Yi Pan, Shizhe Liang, Xiaofeng Yang, Wei Liu, Xiang Li, Fei Dou, Tianming Liu, Jin Lu (* equal contribution)
Proceedings of the 2025 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025
This paper presents HELENE, a memory-efficient and scalable optimizer for fine-tuning large language models, addressing the slow convergence of zeroth-order methods like MeZO by incorporating annealed A-GNB gradients, diagonal Hessian estimation, and layer-wise clipping. HELENE achieves faster, more stable convergence with up to 20× speedup and improved accuracy, and it supports both full and parameter-efficient fine-tuning across large-scale models and tasks.
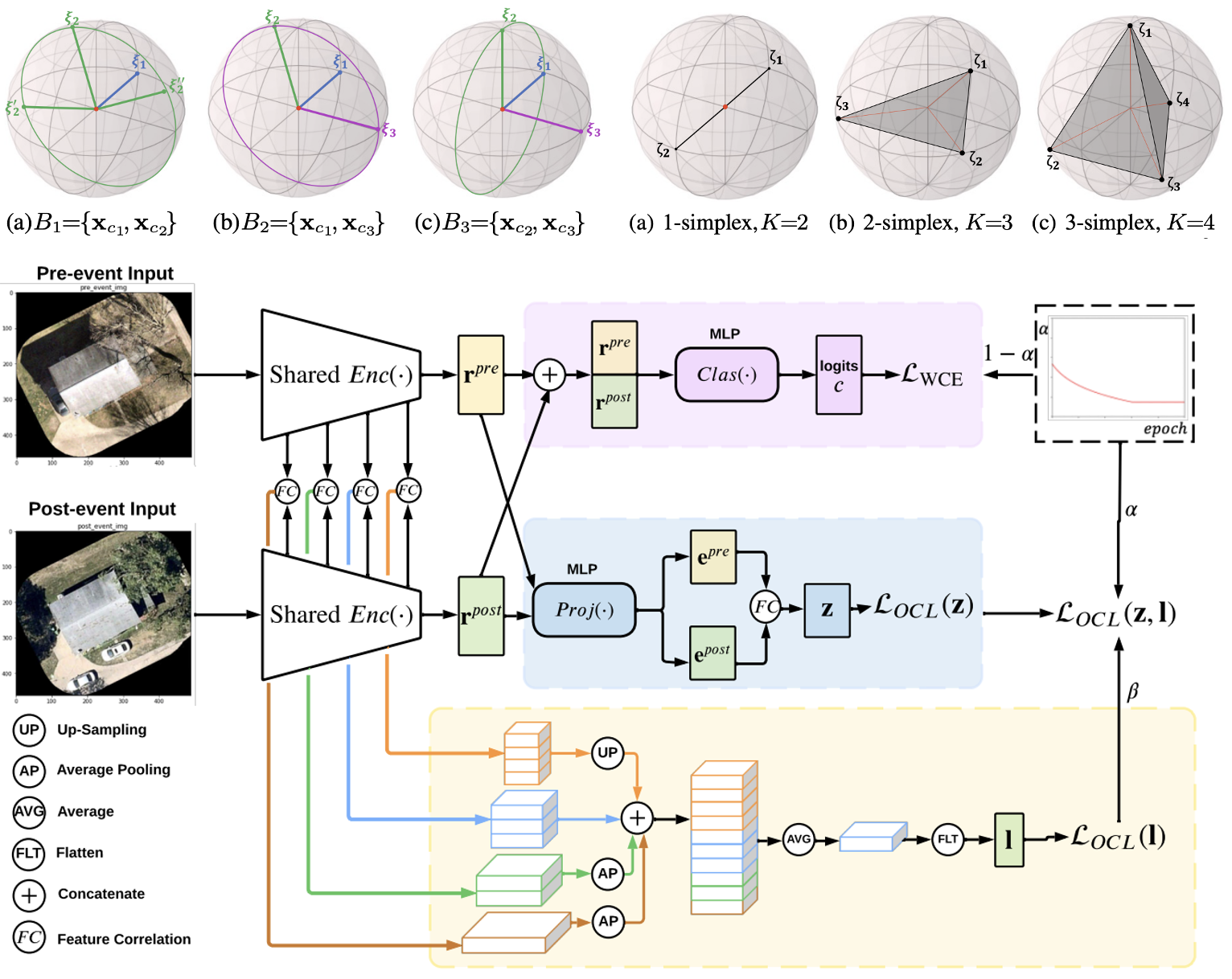
LOCAL: Latent Orthonormal Contrastive Learning for Paired Images
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Tan Zhu, Jinbo Bi
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV Findings, Oral) 2025
This paper introduces Latent Orthonormal Contrastive Learning (LOCAL), a method for paired image classification that addresses limitations of Supervised Contrastive Learning (SCL) under small batch sizes and class imbalance. By mapping class representations to orthogonal planes and incorporating a feature correlation module, LOCAL improves efficiency and discriminative power, achieving superior performance on high-resolution, paired satellite image tasks.
LOCAL: Latent Orthonormal Contrastive Learning for Paired Images
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Tan Zhu, Jinbo Bi
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV Findings, Oral) 2025
This paper introduces Latent Orthonormal Contrastive Learning (LOCAL), a method for paired image classification that addresses limitations of Supervised Contrastive Learning (SCL) under small batch sizes and class imbalance. By mapping class representations to orthogonal planes and incorporating a feature correlation module, LOCAL improves efficiency and discriminative power, achieving superior performance on high-resolution, paired satellite image tasks.
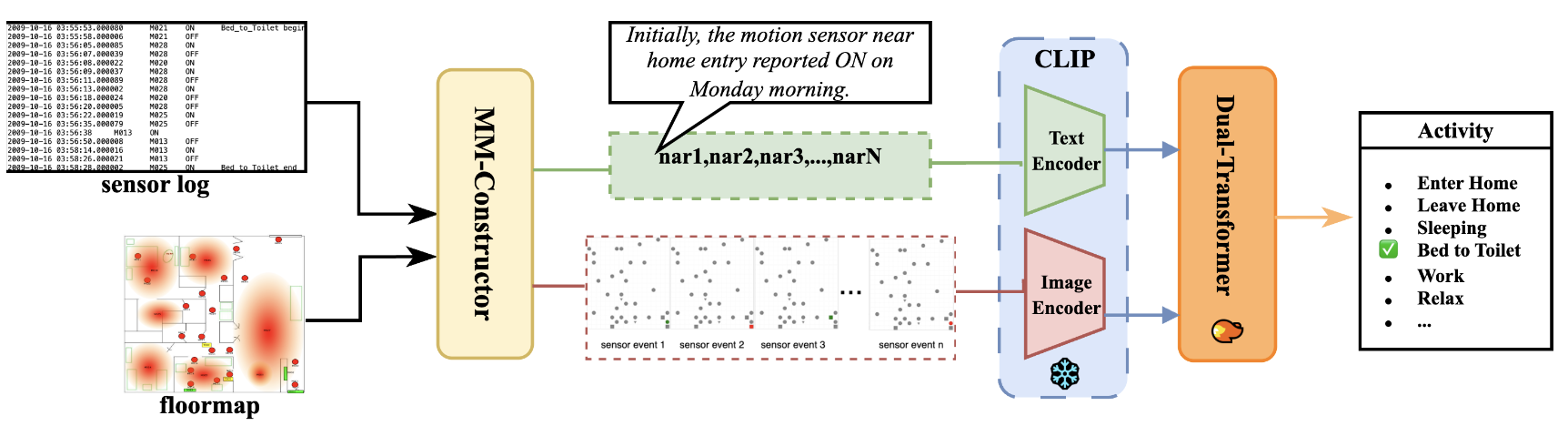
Cross-Modal Translation and Alignment of Sensor Events for Layout-Aware Activity Modeling
Weihang You, Zishuai Liu, Fei Dou
Proceedings of the 2025 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers (UbiComp/ISWC) 2025
This paper presents a cross-modal framework for ADL recognition that jointly models semantic narratives and spatially grounded sensor activations. By projecting sensor states onto floorplan grids and aligning them with natural-language descriptions via a CLIP encoder, then capturing temporal dependencies with a dual-stream model, our approach enables trajectory-aware, layout-adaptive activity understanding across heterogeneous smart home environments.
Cross-Modal Translation and Alignment of Sensor Events for Layout-Aware Activity Modeling
Weihang You, Zishuai Liu, Fei Dou
Proceedings of the 2025 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers (UbiComp/ISWC) 2025
This paper presents a cross-modal framework for ADL recognition that jointly models semantic narratives and spatially grounded sensor activations. By projecting sensor states onto floorplan grids and aligning them with natural-language descriptions via a CLIP encoder, then capturing temporal dependencies with a dual-stream model, our approach enables trajectory-aware, layout-adaptive activity understanding across heterogeneous smart home environments.
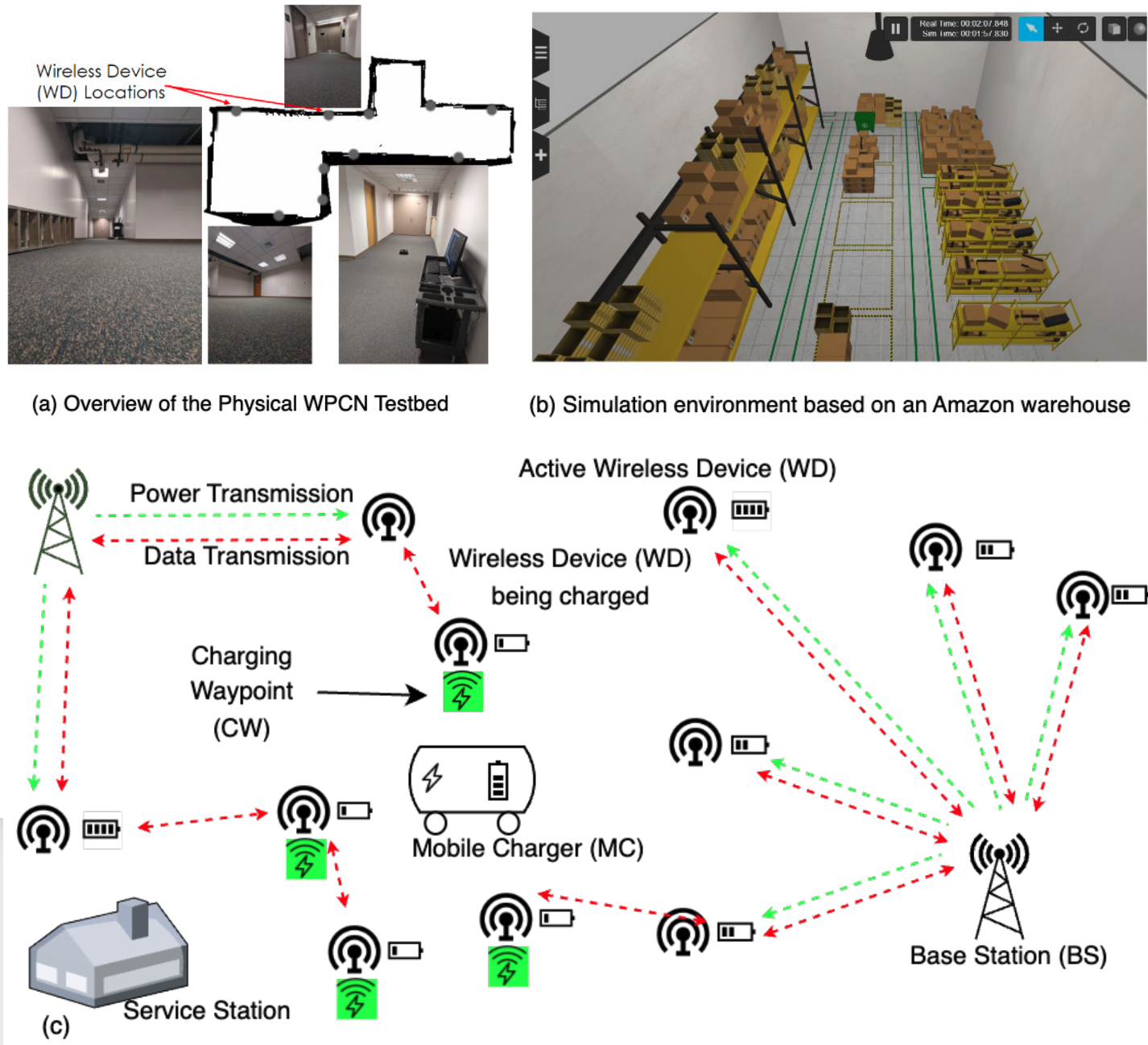
Deep Q-Learning-Based Mobile Charger Path Planning in Wireless Powered Communication Networks
Mainak Mondal, Fei Dou, Jinbo Bi, Song Han
ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS) 2025
This paper presents a reinforcement learning–based framework for wireless charging in Wireless Powered Communication Networks (WPCNs). Using a modified Deep Q-learning approach, the method optimizes a Mobile Charger’s trajectory and device charging schedule to balance residual energy and travel distance. Evaluations on both a Gazebo-based simulator and a Turtlebot testbed show superior performance over classical, optimization-based, and other learning-based baselines.
Deep Q-Learning-Based Mobile Charger Path Planning in Wireless Powered Communication Networks
Mainak Mondal, Fei Dou, Jinbo Bi, Song Han
ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS) 2025
This paper presents a reinforcement learning–based framework for wireless charging in Wireless Powered Communication Networks (WPCNs). Using a modified Deep Q-learning approach, the method optimizes a Mobile Charger’s trajectory and device charging schedule to balance residual energy and travel distance. Evaluations on both a Gazebo-based simulator and a Turtlebot testbed show superior performance over classical, optimization-based, and other learning-based baselines.
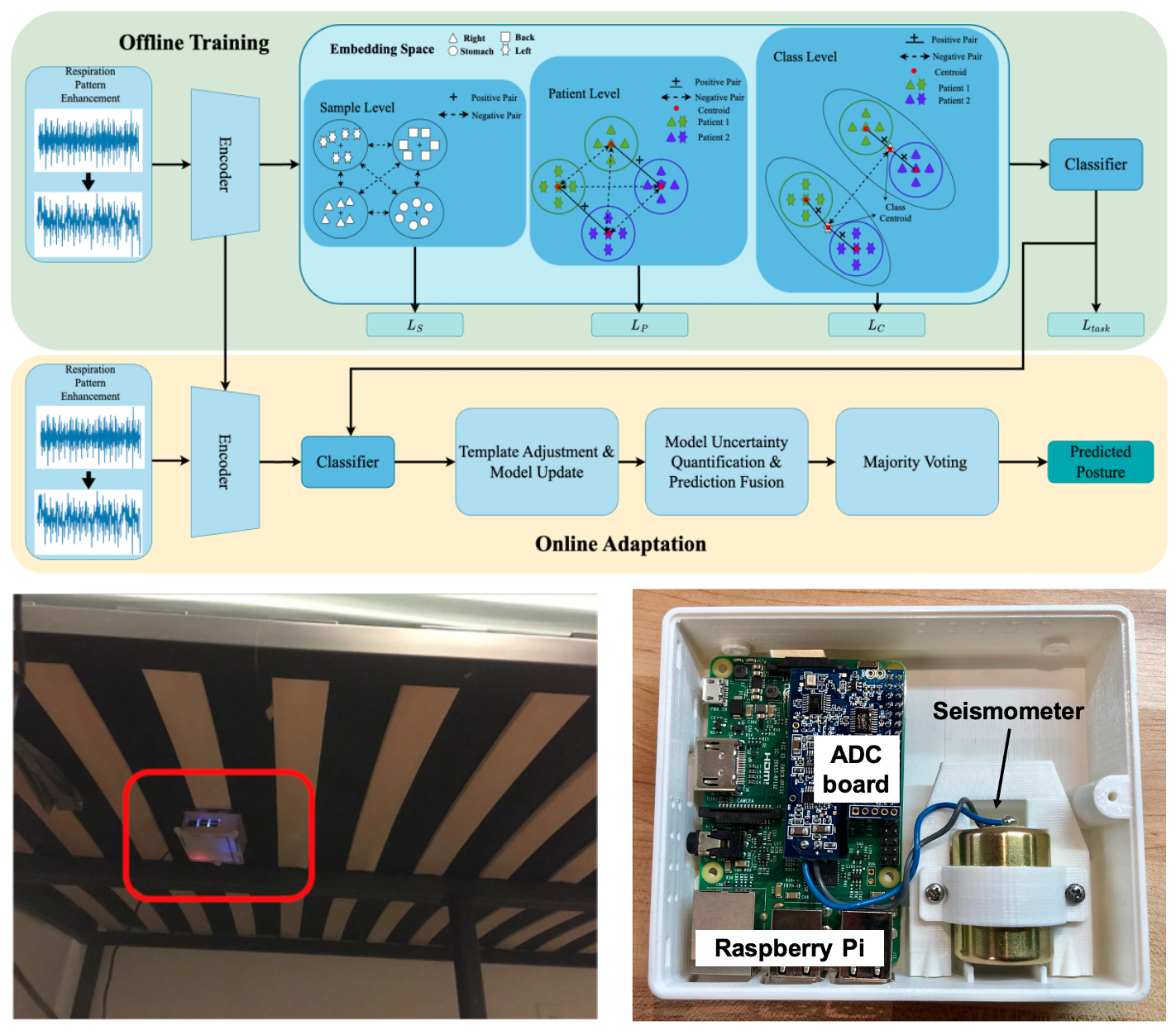
Multi-granularity Supervised Contrastive Learning with Online Adaptation for Contactless In-bed Posture Classification
Yingjian Song, Haotian Xiang, Zixuan Zeng, Jiayu Chen, Yida Zhang, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, He Yang, Qin Lu, Xiang Zhang, Bradley G Phillips, Fei Dou, WenZhan Song
Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (UbiComp/IMWUT) 2025
This paper presents a privacy-friendly, easy-to-deploy in-bed posture classification framework using seismic sensors, integrating a Multi-Granularity Supervised Contrastive Learning (MGSCL) module and an ensemble Online Adaptation (OA) module. The system effectively adapts to individual variations and unlabeled data, achieving high accuracy (91.67%) and F1 score (91.53%) with minimal labeled data in clinical settings, and maintaining strong performance in home environments, highlighting its potential for sleep quality and health monitoring.
Multi-granularity Supervised Contrastive Learning with Online Adaptation for Contactless In-bed Posture Classification
Yingjian Song, Haotian Xiang, Zixuan Zeng, Jiayu Chen, Yida Zhang, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, He Yang, Qin Lu, Xiang Zhang, Bradley G Phillips, Fei Dou, WenZhan Song
Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (UbiComp/IMWUT) 2025
This paper presents a privacy-friendly, easy-to-deploy in-bed posture classification framework using seismic sensors, integrating a Multi-Granularity Supervised Contrastive Learning (MGSCL) module and an ensemble Online Adaptation (OA) module. The system effectively adapts to individual variations and unlabeled data, achieving high accuracy (91.67%) and F1 score (91.53%) with minimal labeled data in clinical settings, and maintaining strong performance in home environments, highlighting its potential for sleep quality and health monitoring.
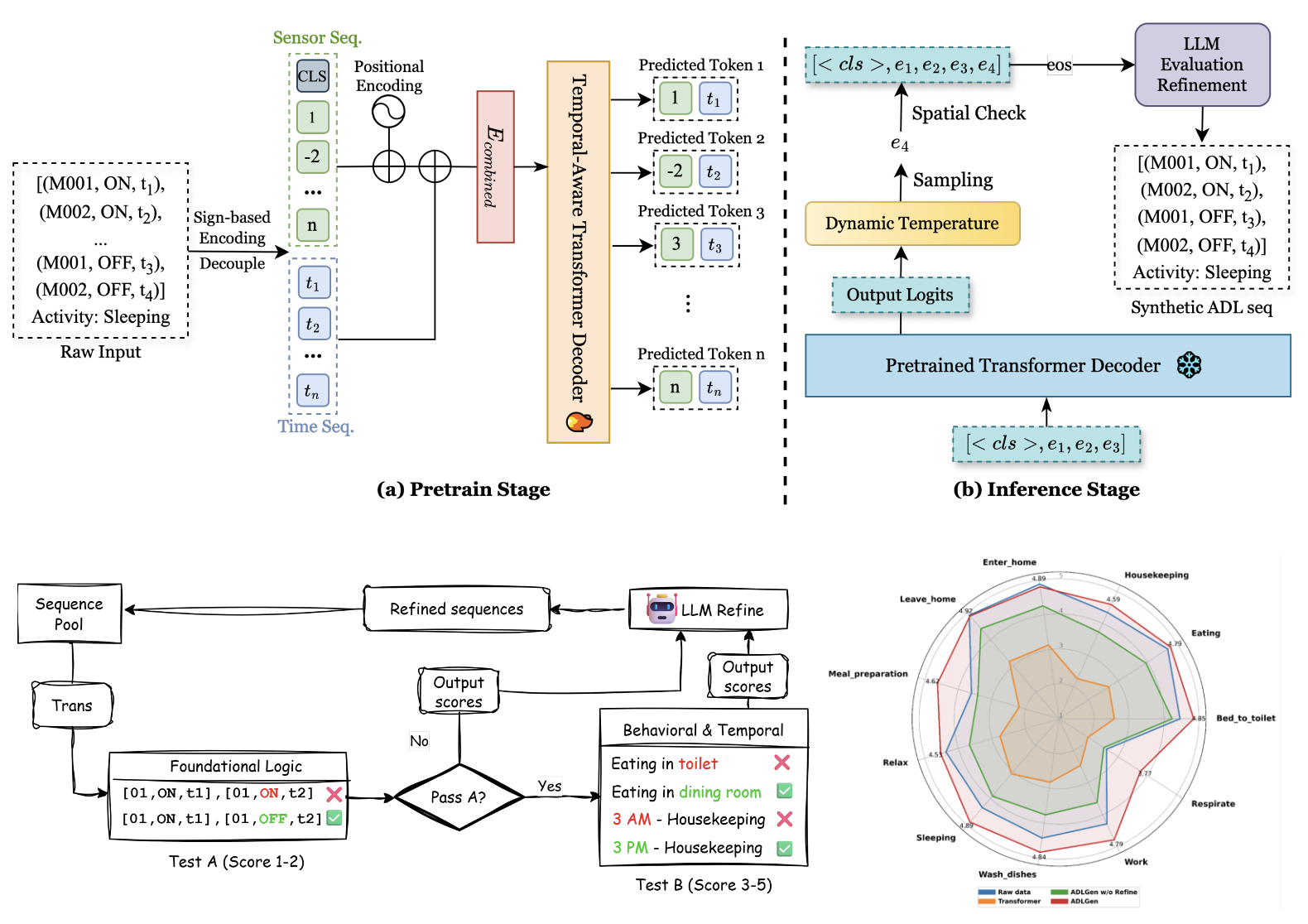
ADLGen: Synthesizing Symbolic, Event-Triggered Sensor Sequences for Human Activity Modeling
Weihang You, Hanqi Jiang, Zishuai Liu, Zihang Xie, Tianming Liu, Jin Lu, Fei Dou
arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.17987 2025
This work introduces ADLGen, a generative framework that synthesizes realistic event-triggered symbolic sensor sequences for ambient assistive environments, addressing the privacy, cost, and sparsity challenges of real-world ADL data collection. ADLGen combines a decoder-only Transformer with sign-based temporal encoding and context-/layout-aware sampling, plus an LLM-driven generate–evaluate–refine loop to enforce logical and temporal coherence without manual tuning. Experiments show ADLGen outperforms baselines in fidelity, semantic richness, and downstream activity recognition.
ADLGen: Synthesizing Symbolic, Event-Triggered Sensor Sequences for Human Activity Modeling
Weihang You, Hanqi Jiang, Zishuai Liu, Zihang Xie, Tianming Liu, Jin Lu, Fei Dou
arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.17987 2025
This work introduces ADLGen, a generative framework that synthesizes realistic event-triggered symbolic sensor sequences for ambient assistive environments, addressing the privacy, cost, and sparsity challenges of real-world ADL data collection. ADLGen combines a decoder-only Transformer with sign-based temporal encoding and context-/layout-aware sampling, plus an LLM-driven generate–evaluate–refine loop to enforce logical and temporal coherence without manual tuning. Experiments show ADLGen outperforms baselines in fidelity, semantic richness, and downstream activity recognition.
2024
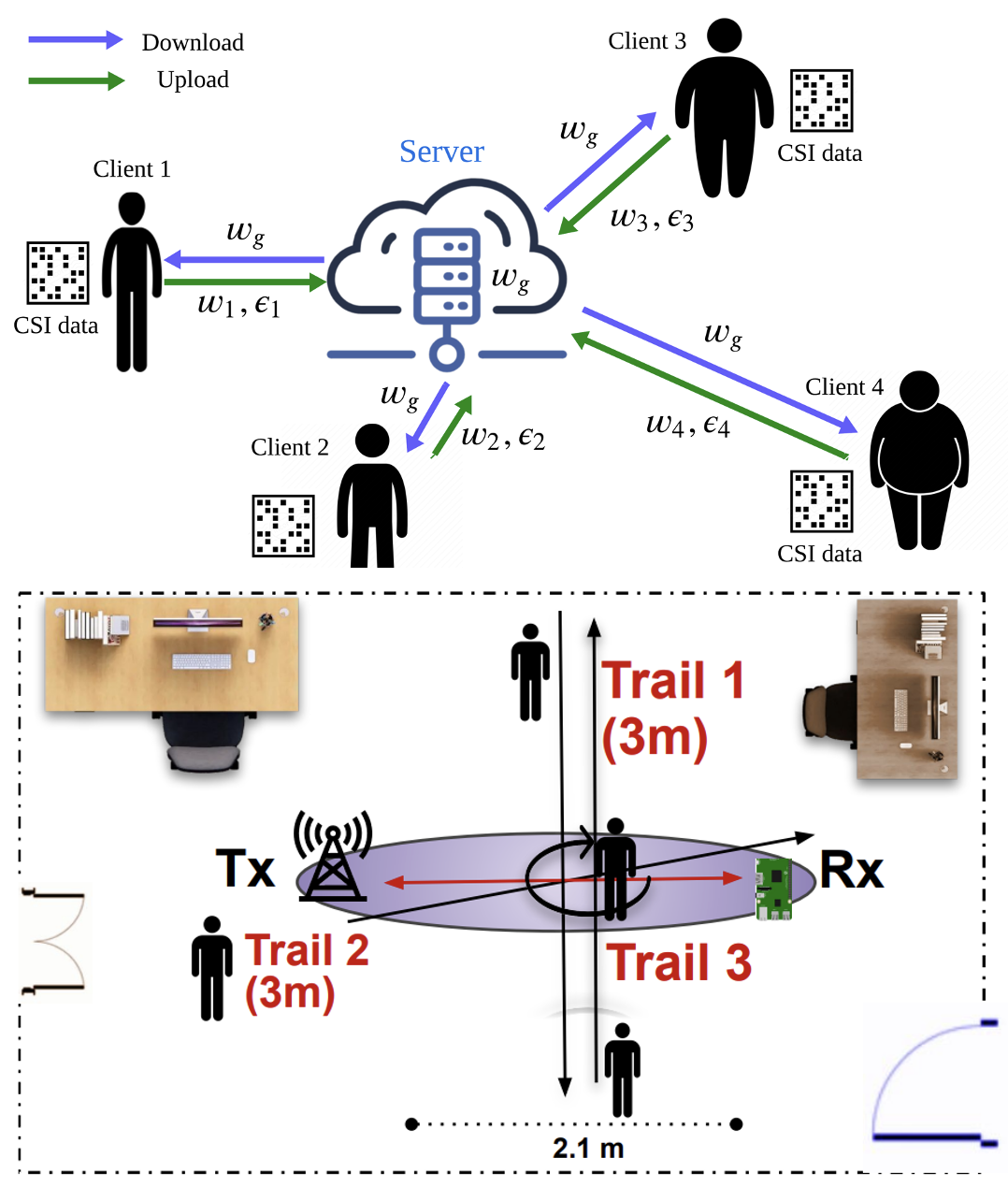
Proximal Federated Learning for Body Mass Index Monitoring using Commodity WiFi
Jiaxi Li, Kiran Davuluri, Khairul Mottakin, Zheng Song, Fei Dou, Jin Lu
ACM MobiCom '24: Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking 2024
This paper proposes a privacy-preserving BMI monitoring system using proximal federated learning (PFL) and commodity WiFi devices, leveraging Channel State Information (CSI) to passively classify BMI without requiring active user participation. The approach, powered by the Adaptive Elastic Stochastic ADMM algorithm, addresses data heterogeneity and connectivity issues, achieving higher accuracy, lower communication costs, and better scalability than existing personalized FL methods.
Proximal Federated Learning for Body Mass Index Monitoring using Commodity WiFi
Jiaxi Li, Kiran Davuluri, Khairul Mottakin, Zheng Song, Fei Dou, Jin Lu
ACM MobiCom '24: Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking 2024
This paper proposes a privacy-preserving BMI monitoring system using proximal federated learning (PFL) and commodity WiFi devices, leveraging Channel State Information (CSI) to passively classify BMI without requiring active user participation. The approach, powered by the Adaptive Elastic Stochastic ADMM algorithm, addresses data heterogeneity and connectivity issues, achieving higher accuracy, lower communication costs, and better scalability than existing personalized FL methods.
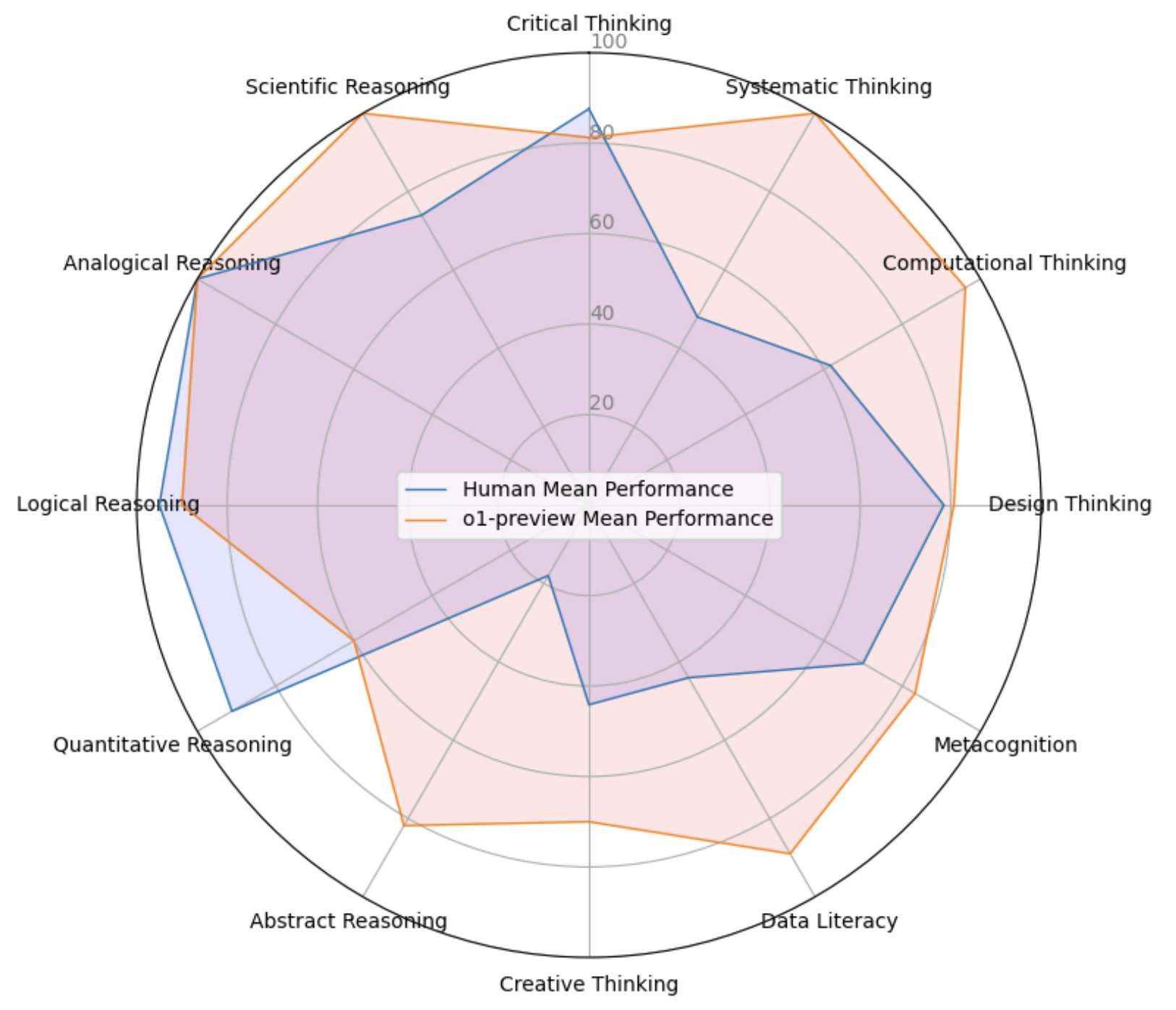
A Systematic Assessment of OpenAI o1-Preview for Higher Order Thinking in Education
Ehsan Latif, Yifan Zhou, Shuchen Guo, Yizhu Gao, Lehong Shi, Matthew Nayaaba, Gyeonggeon Lee, Liang Zhang, Arne Bewersdorff, Luyang Fang, Xiantong Yang, Huaqin Zhao, Hanqi Jiang, Haoran Lu, Jiaxi Li, Jichao Yu, Weihang You, Zhengliang Liu, Vincent Shung Liu, Hui Wang, Zihao Wu, Jin Lu, Fei Dou, Ping Ma, Ninghao Liu, Tianming Liu, Xiaoming Zhai
arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.21287 2024
This study evaluates OpenAI's o1-preview model across 14 higher-order cognitive dimensions, finding it outperforms humans in areas like systems thinking, computational thinking, and creative thinking, while slightly underperforming in logical, critical, and quantitative reasoning. Despite its strengths, the model shows limitations in abstract reasoning, underscoring the need for human oversight and suggesting educational systems should adapt to emphasize uniquely human skills in an AI-enhanced world.
A Systematic Assessment of OpenAI o1-Preview for Higher Order Thinking in Education
Ehsan Latif, Yifan Zhou, Shuchen Guo, Yizhu Gao, Lehong Shi, Matthew Nayaaba, Gyeonggeon Lee, Liang Zhang, Arne Bewersdorff, Luyang Fang, Xiantong Yang, Huaqin Zhao, Hanqi Jiang, Haoran Lu, Jiaxi Li, Jichao Yu, Weihang You, Zhengliang Liu, Vincent Shung Liu, Hui Wang, Zihao Wu, Jin Lu, Fei Dou, Ping Ma, Ninghao Liu, Tianming Liu, Xiaoming Zhai
arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.21287 2024
This study evaluates OpenAI's o1-preview model across 14 higher-order cognitive dimensions, finding it outperforms humans in areas like systems thinking, computational thinking, and creative thinking, while slightly underperforming in logical, critical, and quantitative reasoning. Despite its strengths, the model shows limitations in abstract reasoning, underscoring the need for human oversight and suggesting educational systems should adapt to emphasize uniquely human skills in an AI-enhanced world.
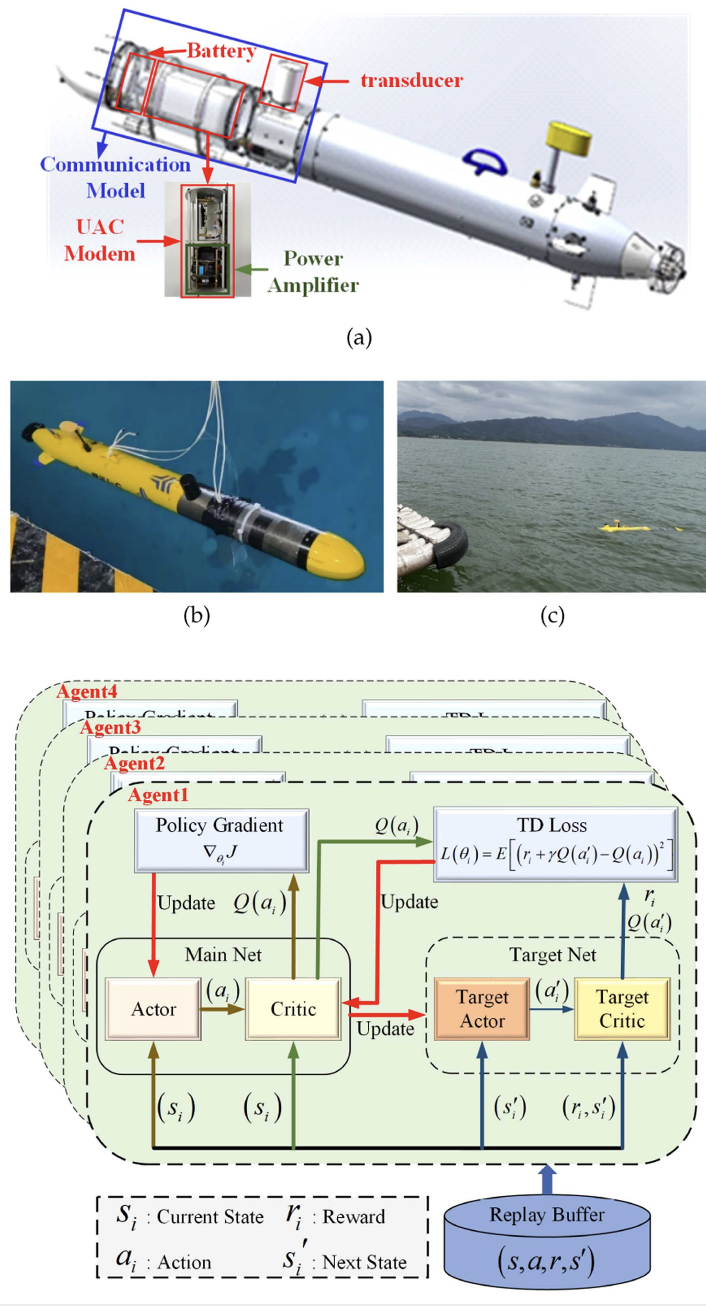
Secure Localization for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks via AUV Cooperative Beamforming With Reinforcement Learning
Rong Fan, Azzedine Boukerche, Pan Pan, Zhigang Jin, Yishan Su, Fei Dou
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) 2024
This paper proposes a secure localization scheme for underwater wireless sensor networks using cooperative beamforming with mobile anchor nodes and TDOA-based self-localization, addressing privacy threats from eavesdroppers. By formulating a multi-objective optimization problem and solving it with a DRL-based MADDPG algorithm, the approach enhances both security and energy efficiency, as validated by simulations and field experiments.
Secure Localization for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks via AUV Cooperative Beamforming With Reinforcement Learning
Rong Fan, Azzedine Boukerche, Pan Pan, Zhigang Jin, Yishan Su, Fei Dou
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) 2024
This paper proposes a secure localization scheme for underwater wireless sensor networks using cooperative beamforming with mobile anchor nodes and TDOA-based self-localization, addressing privacy threats from eavesdroppers. By formulating a multi-objective optimization problem and solving it with a DRL-based MADDPG algorithm, the approach enhances both security and energy efficiency, as validated by simulations and field experiments.
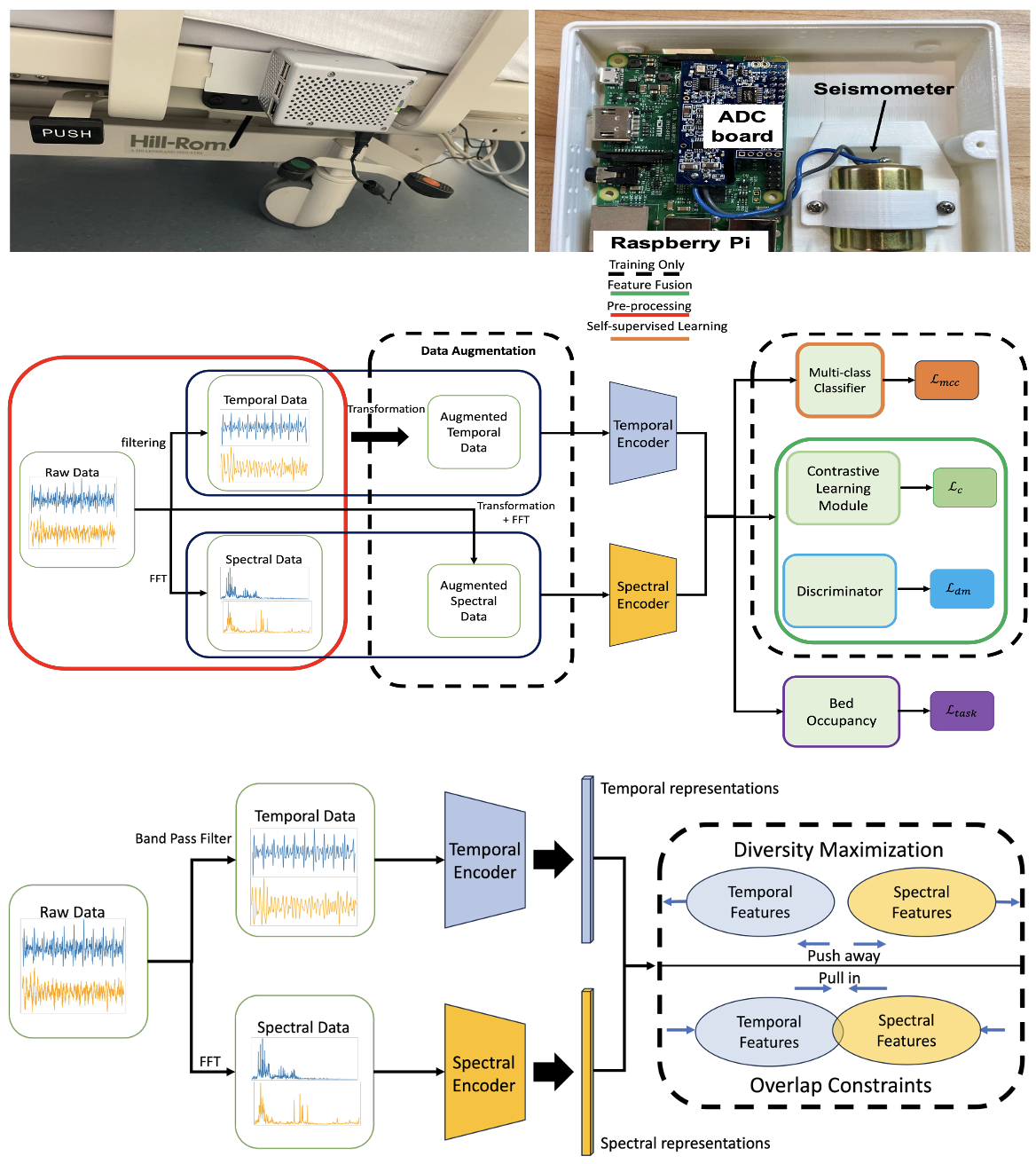
Self-Supervised Representation Learning and Temporal-Spectral Feature Fusion for Bed Occupancy Detection
Yingjian Song, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, Fei Dou, Jin Sun, Xiang Zhang, Bradley G Phillips, WenZhan Song
Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (UbiComp/IMWUT) 2024
This paper presents SeismoDot, a bed occupancy detection system that combines self-supervised learning and spectral-temporal feature fusion to improve generalization across diverse environments with limited data. Unlike traditional threshold-based methods, SeismoDot achieves high accuracy and F1 scores across 13 settings and remains effective even when trained on only 20% of the data, demonstrating strong adaptability and efficiency.
Self-Supervised Representation Learning and Temporal-Spectral Feature Fusion for Bed Occupancy Detection
Yingjian Song, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, Fei Dou, Jin Sun, Xiang Zhang, Bradley G Phillips, WenZhan Song
Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (UbiComp/IMWUT) 2024
This paper presents SeismoDot, a bed occupancy detection system that combines self-supervised learning and spectral-temporal feature fusion to improve generalization across diverse environments with limited data. Unlike traditional threshold-based methods, SeismoDot achieves high accuracy and F1 scores across 13 settings and remains effective even when trained on only 20% of the data, demonstrating strong adaptability and efficiency.
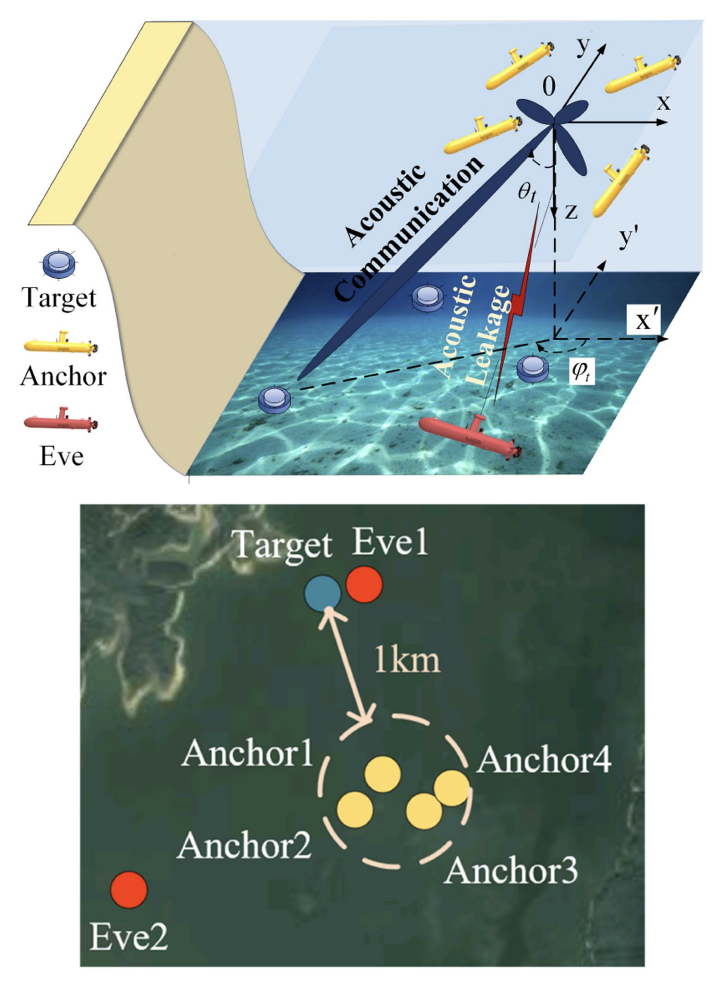
A Secure Localization Scheme for UWSNs based on AUV Formation Cooperative Beamforming
Rong Fan, Pan Pan, Zhigang Jin, Yishan Su, Fei Dou
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) 2024
This paper proposes a secure underwater localization scheme for wireless sensor networks using cooperative beamforming among AUVs and TDOA-based self-localization, addressing the challenge of privacy leakage in acoustic environments. By formulating a multi-objective optimization problem and solving it with a DRL-based MADDPG algorithm, the method enhances both security and energy efficiency, with validation through simulations and sea experiments.
A Secure Localization Scheme for UWSNs based on AUV Formation Cooperative Beamforming
Rong Fan, Pan Pan, Zhigang Jin, Yishan Su, Fei Dou
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) 2024
This paper proposes a secure underwater localization scheme for wireless sensor networks using cooperative beamforming among AUVs and TDOA-based self-localization, addressing the challenge of privacy leakage in acoustic environments. By formulating a multi-objective optimization problem and solving it with a DRL-based MADDPG algorithm, the method enhances both security and energy efficiency, with validation through simulations and sea experiments.
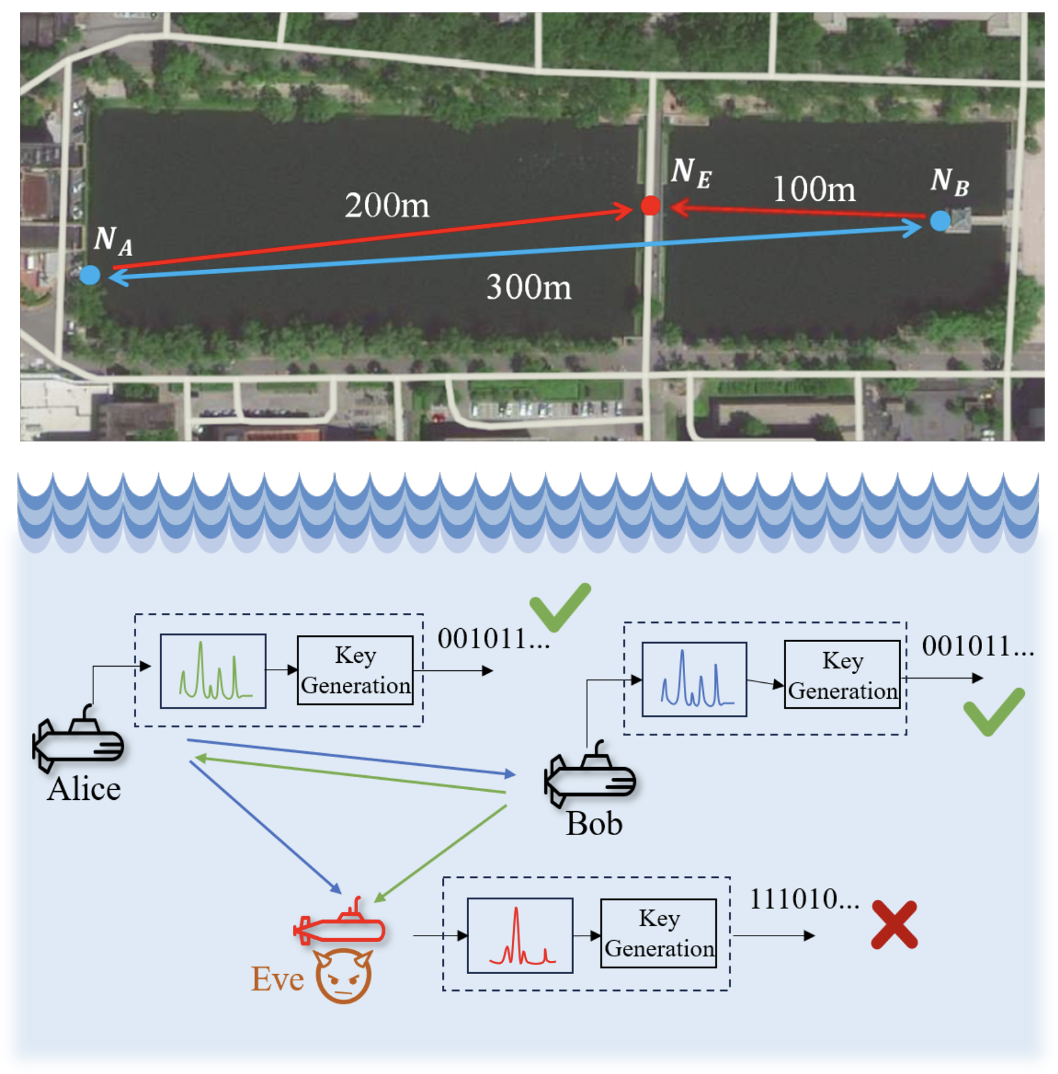
A Secure Communication Scheme Based on Spatio-temporal Dynamics of Underwater Acoustic Channel
Yishan Su, Pan Pan, Rong Fan, Sidan Yang, Fei Dou
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) 2024
This article proposes a secure key generation scheme for underwater acoustic communications that leverages the spatio-temporal dynamics of channel impulse responses (CIRs), using amplitude and time delay as raw key parameters. A synchronous probing protocol enhances channel reciprocity, and field experiments confirm the scheme’s effectiveness and improved performance in resource-constrained underwater environments.
A Secure Communication Scheme Based on Spatio-temporal Dynamics of Underwater Acoustic Channel
Yishan Su, Pan Pan, Rong Fan, Sidan Yang, Fei Dou
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) 2024
This article proposes a secure key generation scheme for underwater acoustic communications that leverages the spatio-temporal dynamics of channel impulse responses (CIRs), using amplitude and time delay as raw key parameters. A synchronous probing protocol enhances channel reciprocity, and field experiments confirm the scheme’s effectiveness and improved performance in resource-constrained underwater environments.
2023
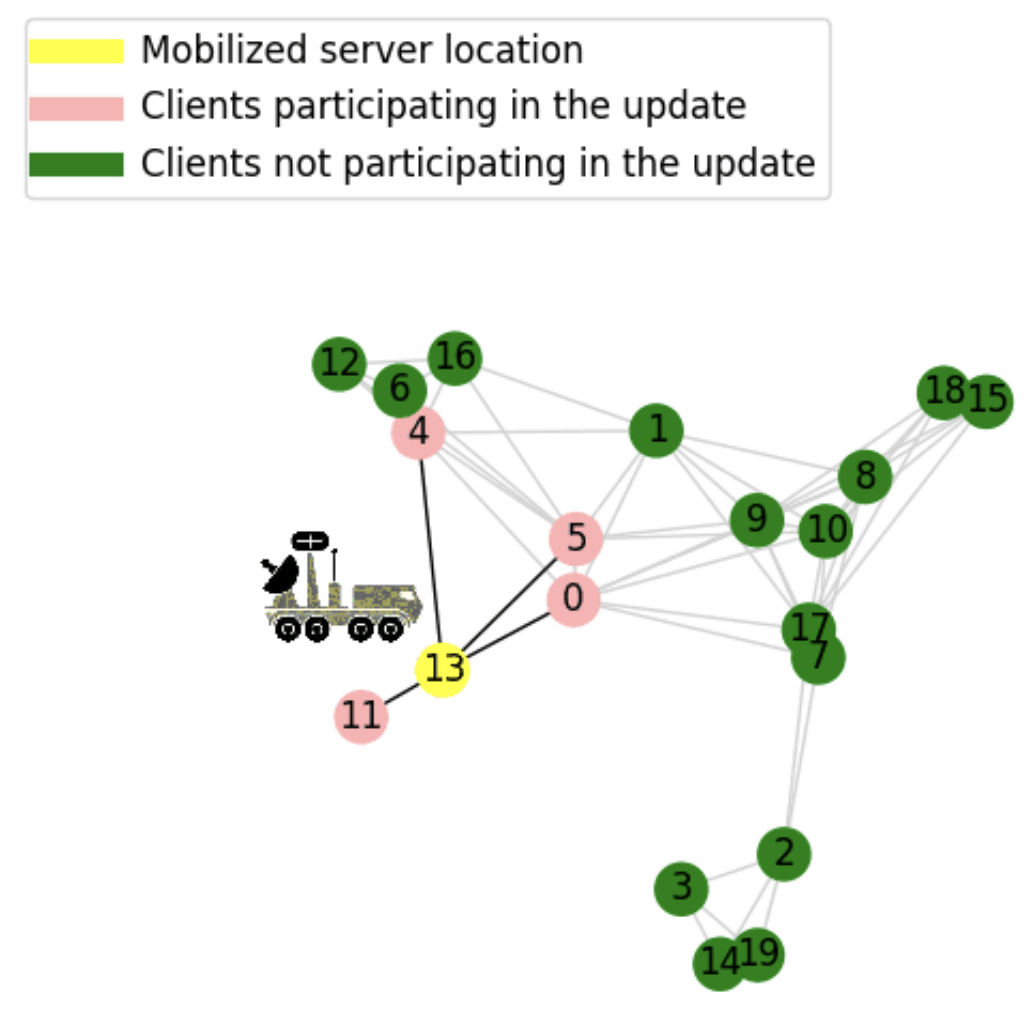
Mobilizing Personalized Federated Learning in Infrastructure-Less and Heterogeneous Environments via Random Walk Stochastic ADMM
Ziba Parsons, Fei Dou, Houyi Du, Zheng Song, Jin Lu
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 (NeurIPS) 2023
This paper proposes RWSADMM, a novel federated learning algorithm designed for infrastructure-less environments with isolated, heterogeneous nodes connected via wireless links. By leveraging server mobility and enforcing hard constraints among adjacent clients, RWSADMM enables efficient, personalized learning with provable convergence, reduced communication costs, and improved accuracy and scalability over baseline methods.
Mobilizing Personalized Federated Learning in Infrastructure-Less and Heterogeneous Environments via Random Walk Stochastic ADMM
Ziba Parsons, Fei Dou, Houyi Du, Zheng Song, Jin Lu
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 (NeurIPS) 2023
This paper proposes RWSADMM, a novel federated learning algorithm designed for infrastructure-less environments with isolated, heterogeneous nodes connected via wireless links. By leveraging server mobility and enforcing hard constraints among adjacent clients, RWSADMM enables efficient, personalized learning with provable convergence, reduced communication costs, and improved accuracy and scalability over baseline methods.
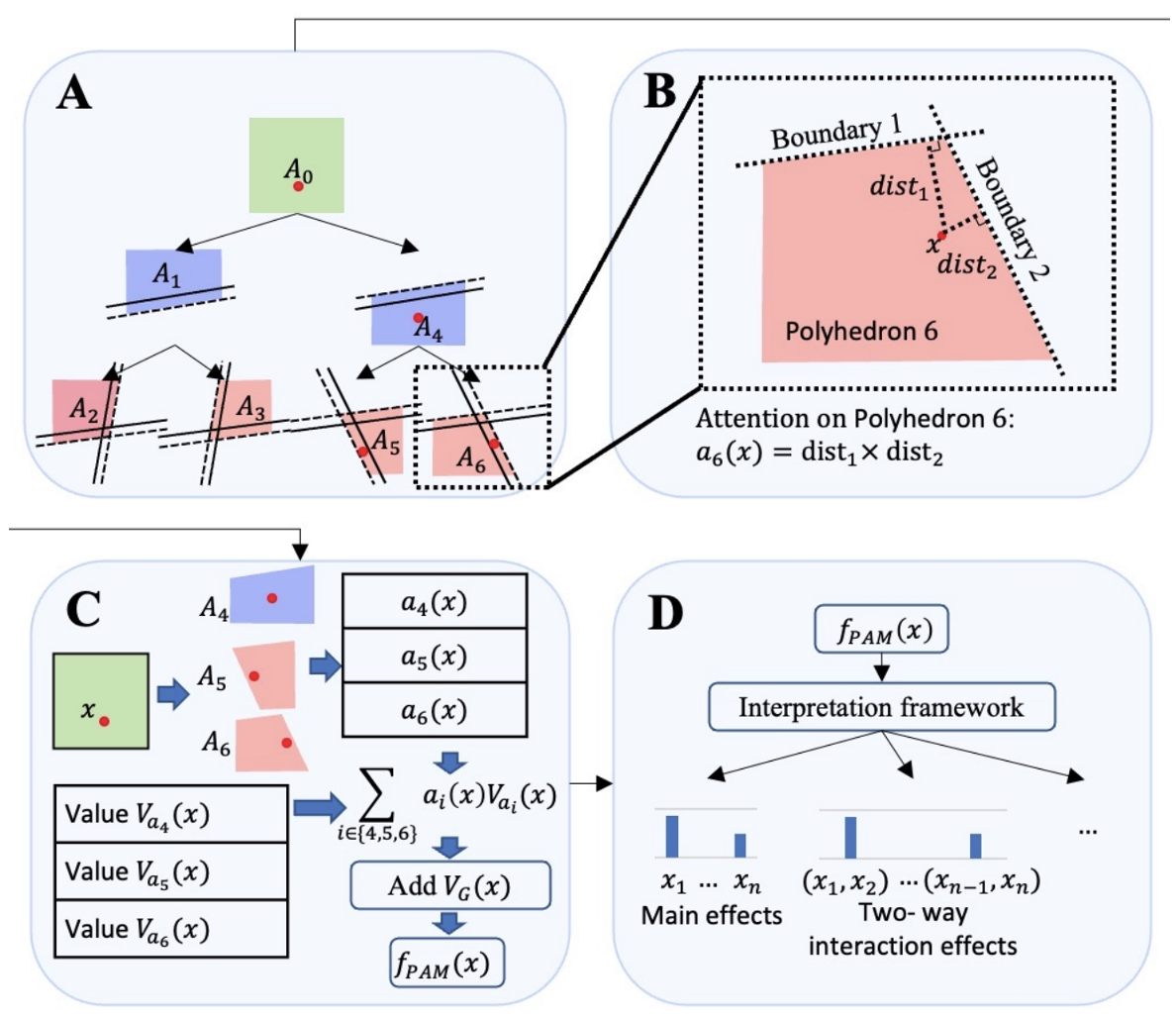
Polyhedron Attention Module: Learning Adaptive-order Interactions
Tan Zhu, Fei Dou, Xinyu Wang, Jin Lu, Jinbo Bi
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 (NeurIPS) 2023
This paper introduces the Polyhedron Attention Module (PAM), which forms interpretable, piecewise polynomial models by adaptively learning feature interactions within polyhedrons in the input space. PAM outperforms ReLU-based networks in expressive power and achieves superior classification results on large-scale click-through rate datasets while uncovering meaningful interactions in medical applications.
Polyhedron Attention Module: Learning Adaptive-order Interactions
Tan Zhu, Fei Dou, Xinyu Wang, Jin Lu, Jinbo Bi
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 (NeurIPS) 2023
This paper introduces the Polyhedron Attention Module (PAM), which forms interpretable, piecewise polynomial models by adaptively learning feature interactions within polyhedrons in the input space. PAM outperforms ReLU-based networks in expressive power and achieves superior classification results on large-scale click-through rate datasets while uncovering meaningful interactions in medical applications.
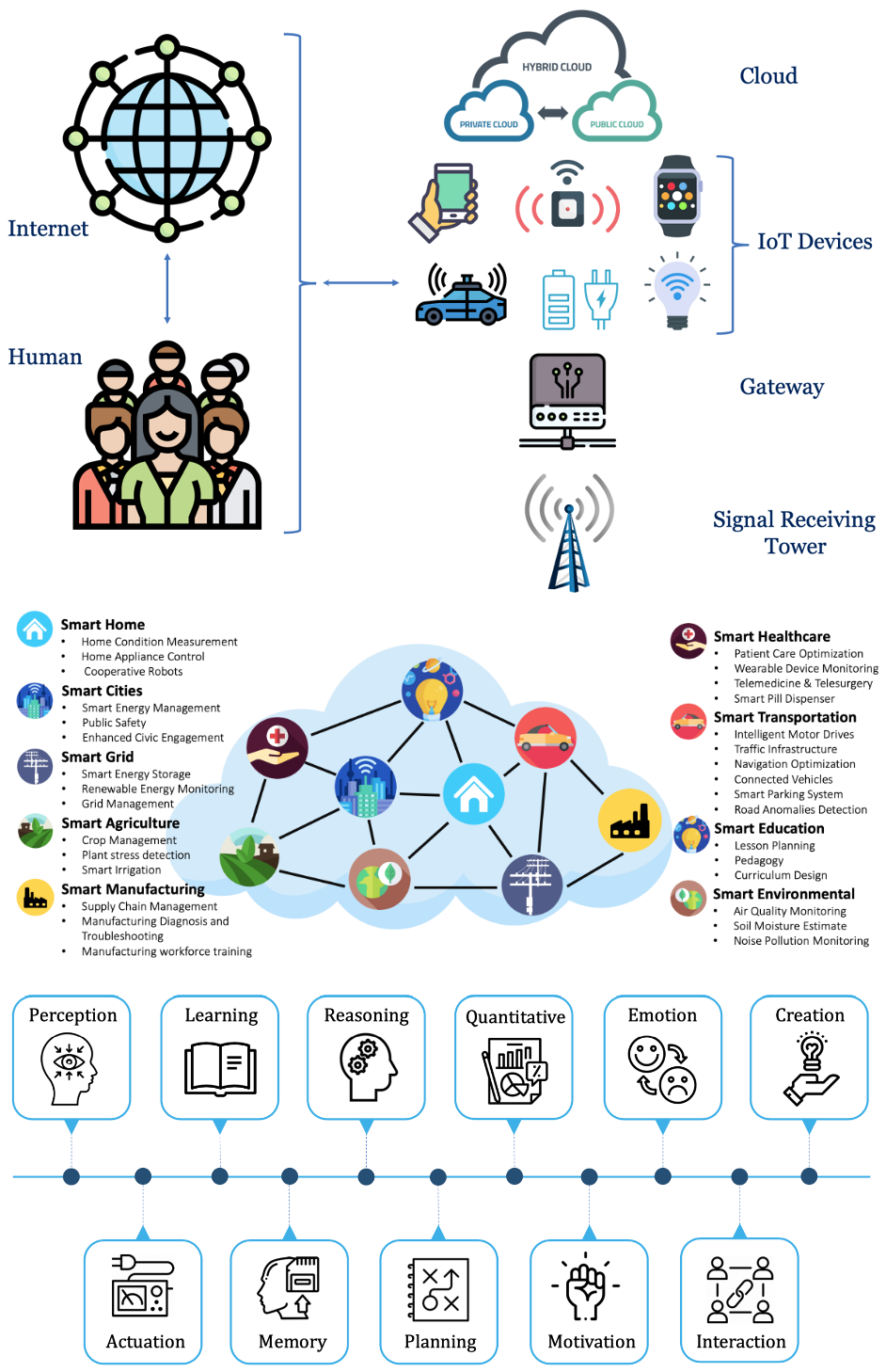
Towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) in the Internet of Things (IoT): Opportunities and Challenges
Fei Dou, Jin Ye, Geng Yuan, Qin Lu, Wei Niu, Haijian Sun, Le Guan, Guoyu Lu, Gengchen Mai, Ninghao Liu, Jin Lu, Zhengliang Liu, Zihao Wu, Chenjiao Tan, Shaochen Xu, Xianqiao Wang, Guoming Li, Lilong Chai, Sheng Li, Jin Sun, Hongyue Sun, Yunli Shao, Changying Li, Tianming Liu, Wenzhan Song
arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07438 2023
This paper investigates the integration of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) within the Internet of Things (IoT), proposing a conceptual framework that highlights AGI’s potential to enhance intelligent decision-making across diverse domains such as healthcare, agriculture, and smart infrastructure. It also examines key challenges, including limited computational resources, large-scale communication complexities, and security and privacy concerns, emphasizing the need for targeted research to adapt AGI for resource-constrained IoT environments.
Towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) in the Internet of Things (IoT): Opportunities and Challenges
Fei Dou, Jin Ye, Geng Yuan, Qin Lu, Wei Niu, Haijian Sun, Le Guan, Guoyu Lu, Gengchen Mai, Ninghao Liu, Jin Lu, Zhengliang Liu, Zihao Wu, Chenjiao Tan, Shaochen Xu, Xianqiao Wang, Guoming Li, Lilong Chai, Sheng Li, Jin Sun, Hongyue Sun, Yunli Shao, Changying Li, Tianming Liu, Wenzhan Song
arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07438 2023
This paper investigates the integration of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) within the Internet of Things (IoT), proposing a conceptual framework that highlights AGI’s potential to enhance intelligent decision-making across diverse domains such as healthcare, agriculture, and smart infrastructure. It also examines key challenges, including limited computational resources, large-scale communication complexities, and security and privacy concerns, emphasizing the need for targeted research to adapt AGI for resource-constrained IoT environments.
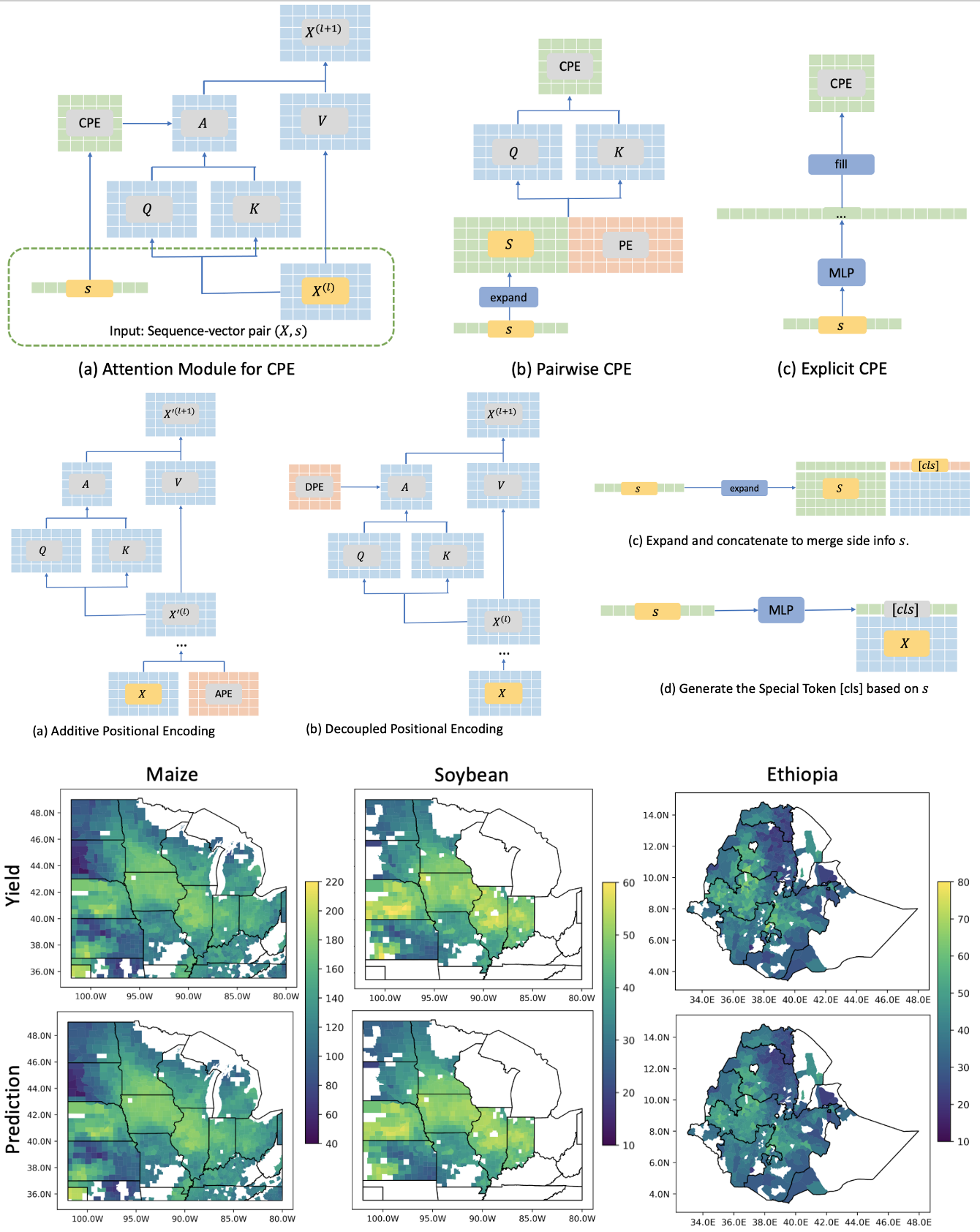
Customized Positional Encoding to Combine Static and Time-varying Data in Robust Representation Learning for Crop Yield Prediction
Qinqing Liu, Fei Dou, Meijian Yang, Ezana Amdework, Guiling Wang, Jinbo Bi
the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) 2023
This paper introduces a novel Transformer-based architecture for crop yield prediction that incorporates Customized Positional Encoding (CPE), adapting sequence encoding based on static variables like geographic location. By leveraging CPE and partially linearized attention, the model significantly improves prediction robustness under climate variability, reducing mean absolute error by up to 26% compared to baseline models during extreme drought years.
Customized Positional Encoding to Combine Static and Time-varying Data in Robust Representation Learning for Crop Yield Prediction
Qinqing Liu, Fei Dou, Meijian Yang, Ezana Amdework, Guiling Wang, Jinbo Bi
the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) 2023
This paper introduces a novel Transformer-based architecture for crop yield prediction that incorporates Customized Positional Encoding (CPE), adapting sequence encoding based on static variables like geographic location. By leveraging CPE and partially linearized attention, the model significantly improves prediction robustness under climate variability, reducing mean absolute error by up to 26% compared to baseline models during extreme drought years.
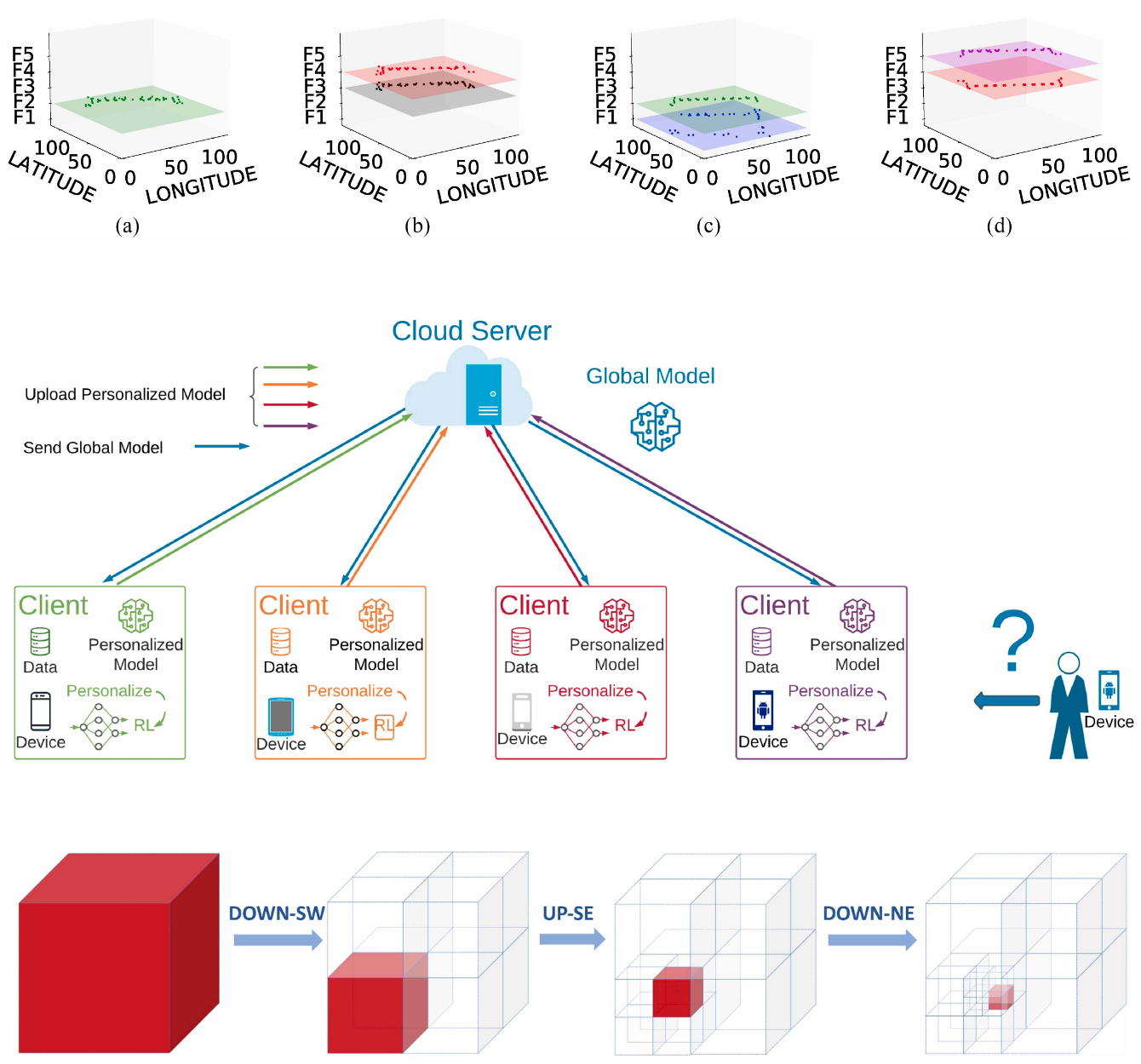
On-Device Indoor Positioning: A Federated Reinforcement Learning Approach With Heterogeneous Devices
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Tan Zhu, Jinbo Bi
IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IOT-J) 2023
This paper proposes a personalized federated reinforcement learning (RL) framework for indoor localization that enables mobile devices to train locally while preserving data privacy and coping with limited connectivity and data heterogeneity. By combining personalized on-device RL with a global model trained via sparse updates, the approach achieves improved localization accuracy and robustness, and is further extended to support few-shot learning for rapid adaptation to new users with minimal data.
On-Device Indoor Positioning: A Federated Reinforcement Learning Approach With Heterogeneous Devices
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Tan Zhu, Jinbo Bi
IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IOT-J) 2023
This paper proposes a personalized federated reinforcement learning (RL) framework for indoor localization that enables mobile devices to train locally while preserving data privacy and coping with limited connectivity and data heterogeneity. By combining personalized on-device RL with a global model trained via sparse updates, the approach achieves improved localization accuracy and robustness, and is further extended to support few-shot learning for rapid adaptation to new users with minimal data.
Before 2023
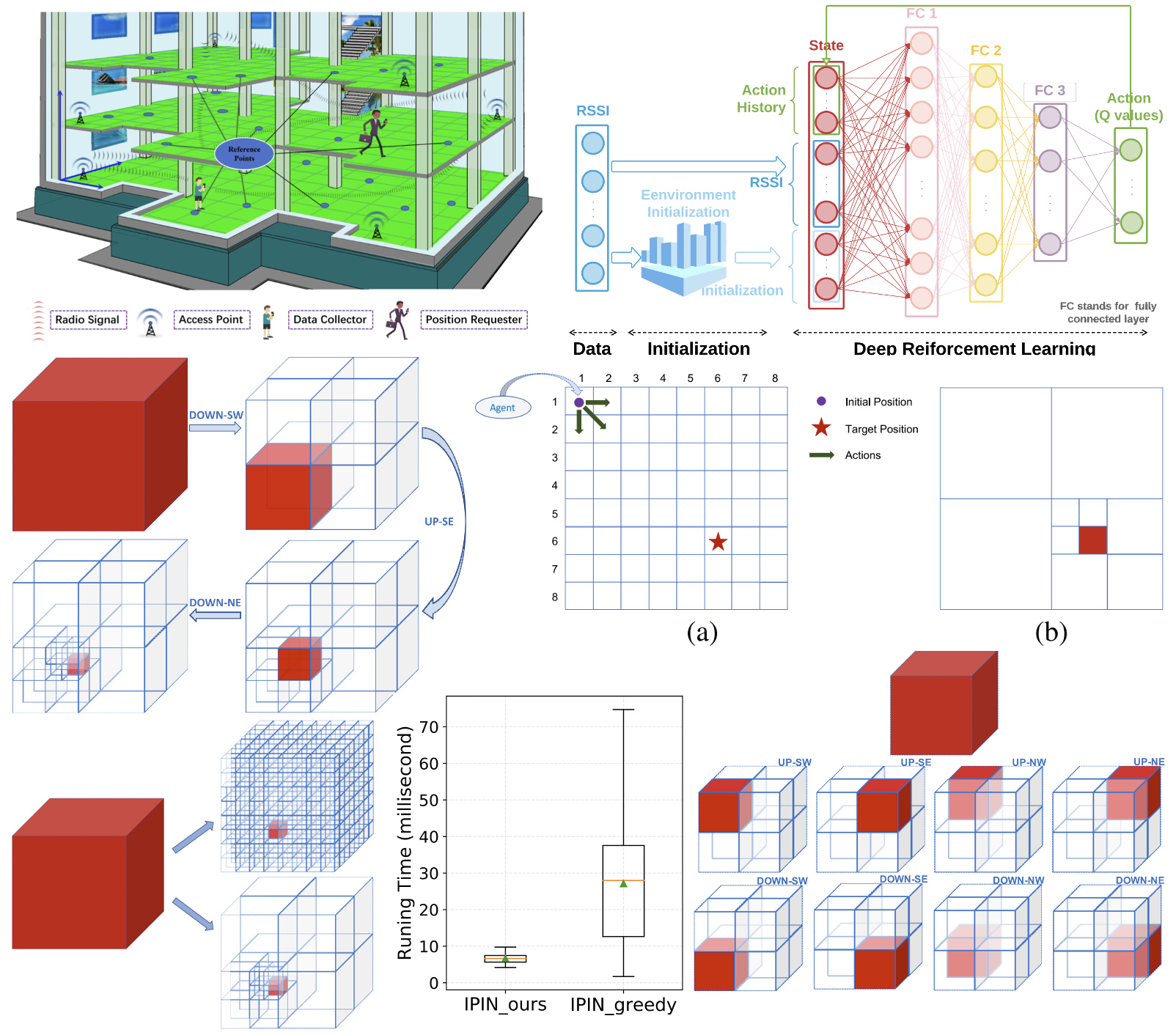
A Bisection Reinforcement Learning Approach to 3D Indoor Localization
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Tingyang Xu, Chun-Hsi Huang, Jinbo Bi
IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IOT-J) 2021
This article presents a deep reinforcement learning-based approach to 3-D indoor localization using Wi-Fi RSSI fingerprinting, addressing signal variability and environmental dynamics. By formulating localization as a Markov decision process and hierarchically bisecting the search space, the method achieves high accuracy and robustness while reducing time complexity from O(N3) to O(log N), outperforming traditional sequential localization methods.
A Bisection Reinforcement Learning Approach to 3D Indoor Localization
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Tingyang Xu, Chun-Hsi Huang, Jinbo Bi
IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IOT-J) 2021
This article presents a deep reinforcement learning-based approach to 3-D indoor localization using Wi-Fi RSSI fingerprinting, addressing signal variability and environmental dynamics. By formulating localization as a Markov decision process and hierarchically bisecting the search space, the method achieves high accuracy and robustness while reducing time complexity from O(N3) to O(log N), outperforming traditional sequential localization methods.
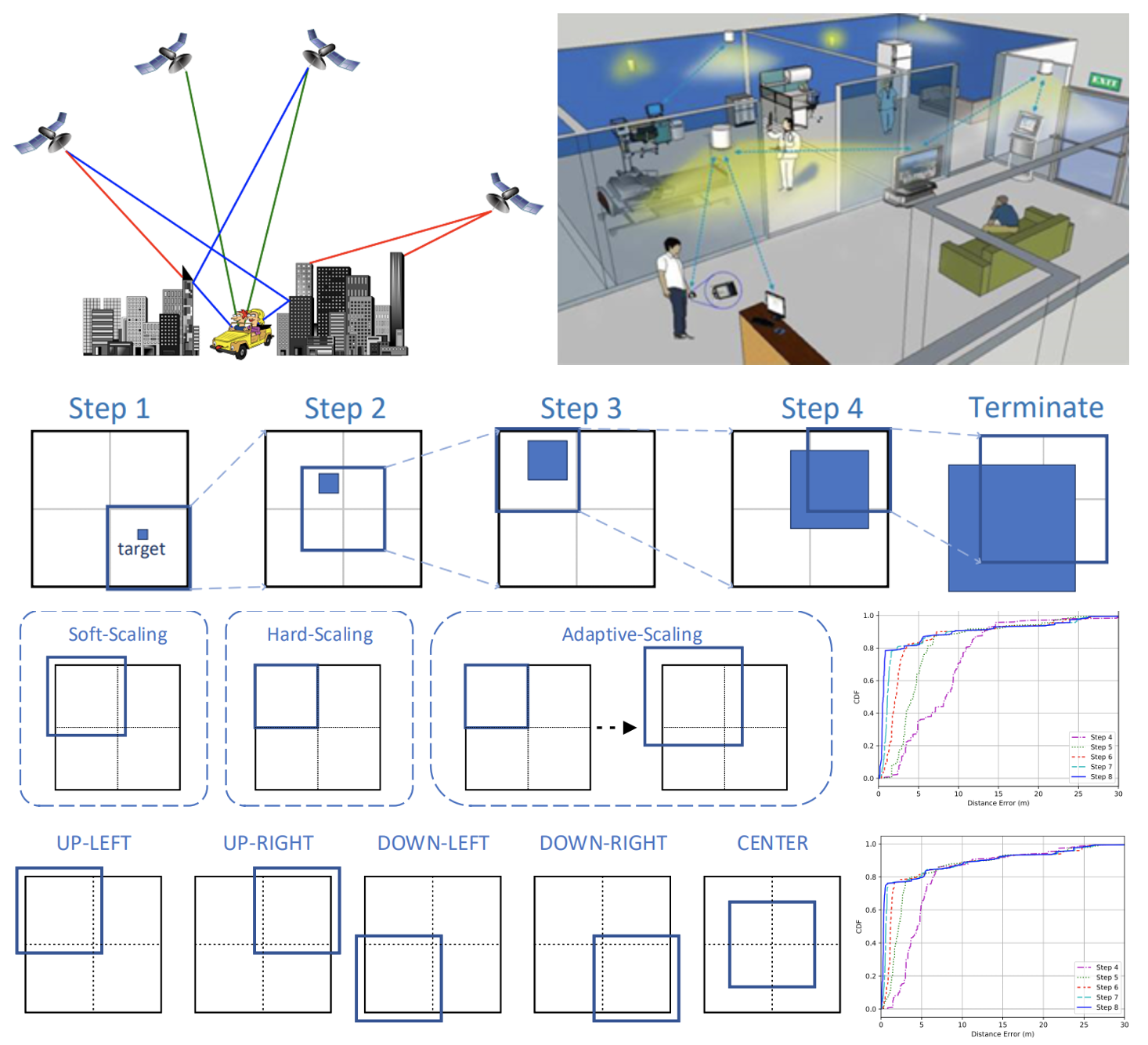
Top-Down Indoor Localization with Wi-Fi Fingerprints Using Deep Q-Network
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Xia Xiao, Zigeng Wang, Jinbo Bi, Chun-Hsi Huang
IEEE 15th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS) 2018
This paper proposes a deep reinforcement learning-based top-down searching method for indoor localization using Wi-Fi RSSI fingerprints, addressing signal fluctuations caused by environmental uncertainties. The model effectively navigates large indoor spaces, accurately localizing 75% of targets within 0.55 meters in a 25,000 m² area.
Top-Down Indoor Localization with Wi-Fi Fingerprints Using Deep Q-Network
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Xia Xiao, Zigeng Wang, Jinbo Bi, Chun-Hsi Huang
IEEE 15th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS) 2018
This paper proposes a deep reinforcement learning-based top-down searching method for indoor localization using Wi-Fi RSSI fingerprints, addressing signal fluctuations caused by environmental uncertainties. The model effectively navigates large indoor spaces, accurately localizing 75% of targets within 0.55 meters in a 25,000 m² area.
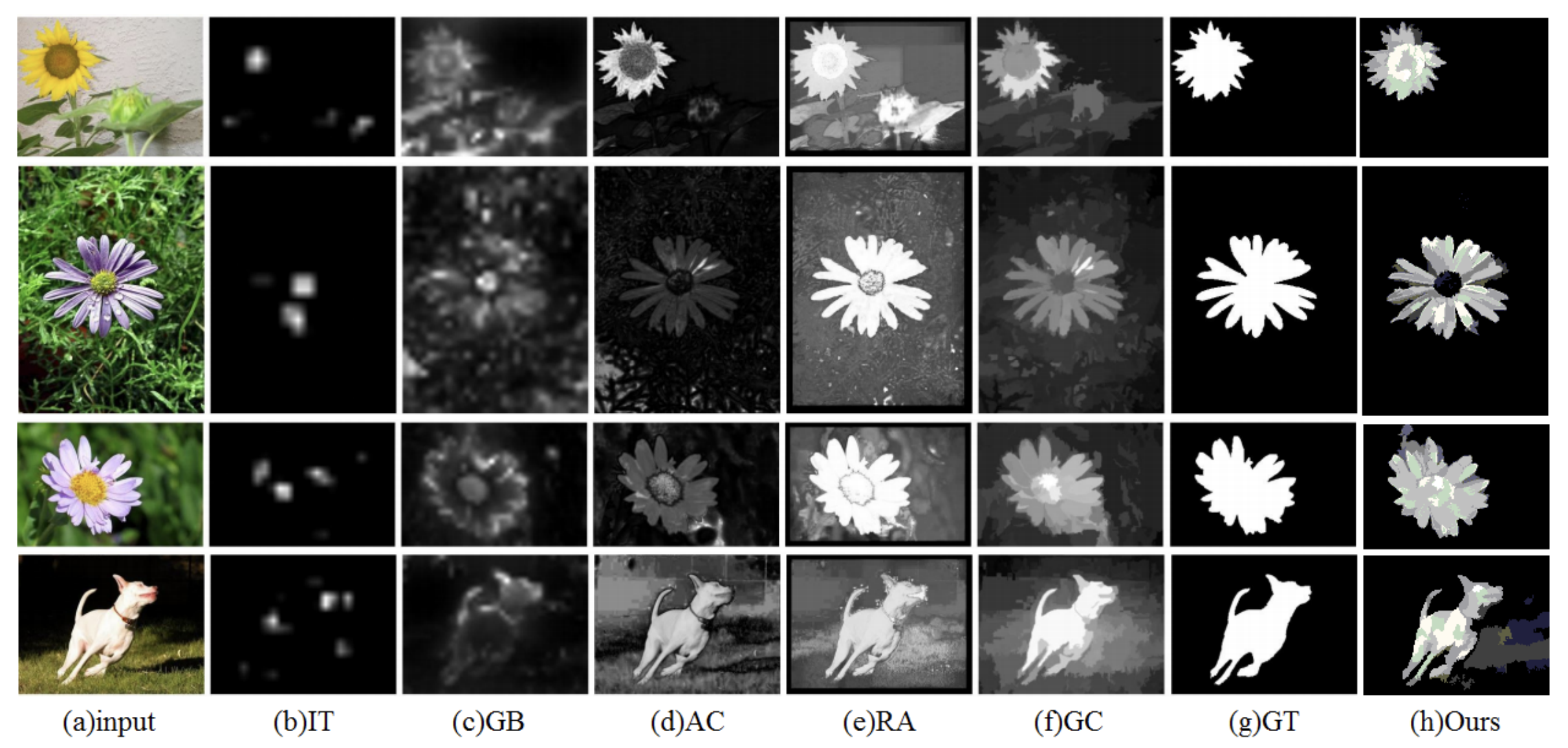

Bi-Subspace Saliency Detection
Jin Lu, Fei Dou
IEEE 7th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC) 2017
This paper introduces a bi-subspace bottom-up saliency detection model that separates background and salient objects through subspace analysis, incorporating group-sparse constraints to capture object structure. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves greater stability and accuracy compared to existing saliency detection methods.
Bi-Subspace Saliency Detection
Jin Lu, Fei Dou
IEEE 7th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC) 2017
This paper introduces a bi-subspace bottom-up saliency detection model that separates background and salient objects through subspace analysis, incorporating group-sparse constraints to capture object structure. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves greater stability and accuracy compared to existing saliency detection methods.
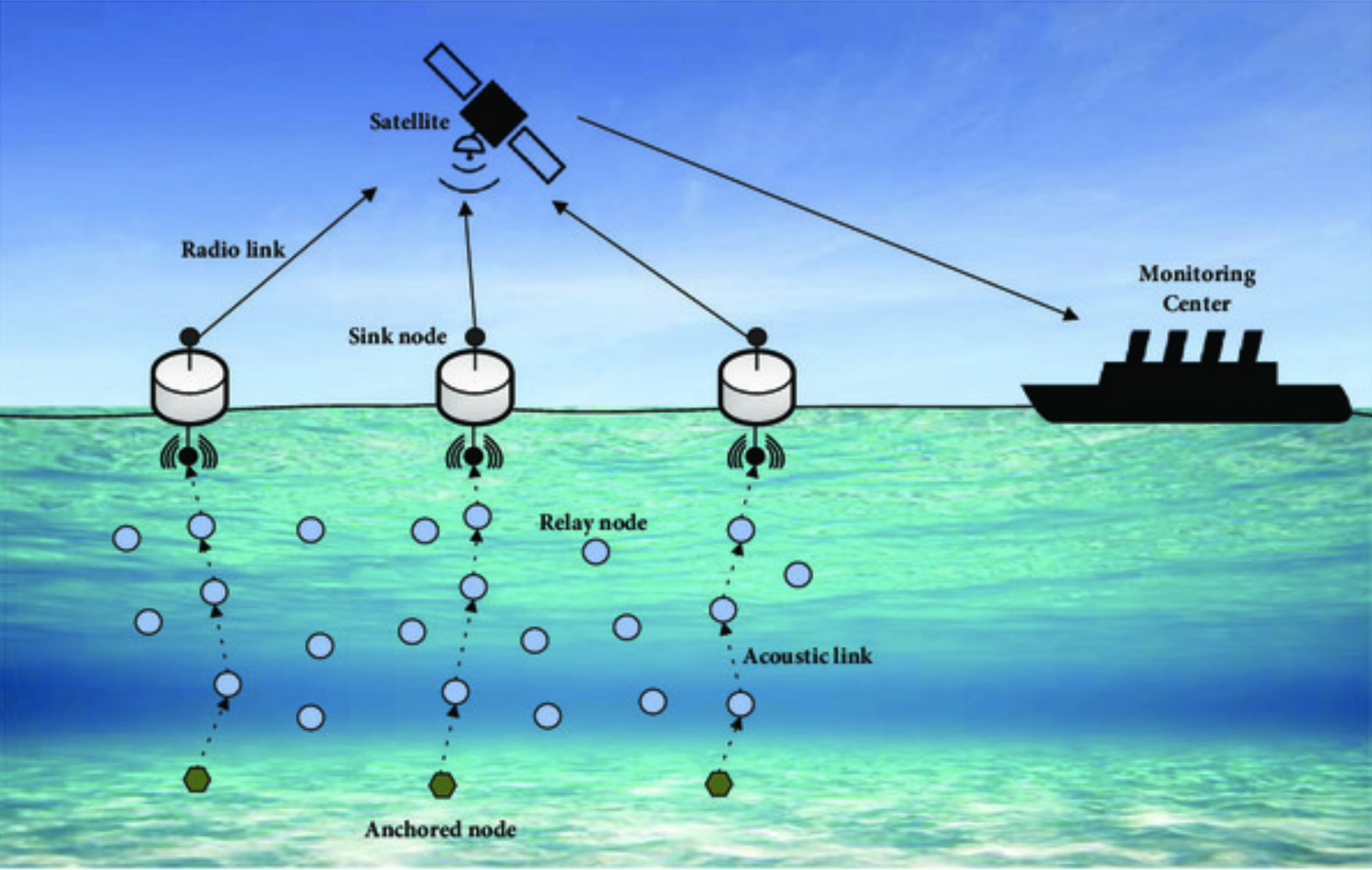
On-demand Pipelined MAC for Multi-hop Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks
Fei Dou, Zheng Peng
Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems (WUWNet) 2015
This paper proposes OPMAC, a new medium access control (MAC) protocol designed for time-critical applications in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks (UWSNs). By establishing an on-demand data transmission pipeline and introducing a lightweight acknowledgment mechanism, OPMAC significantly reduces end-to-end delay and enhances energy efficiency, addressing the challenges of long propagation delays and high error rates in UWSNs.
On-demand Pipelined MAC for Multi-hop Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks
Fei Dou, Zheng Peng
Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems (WUWNet) 2015
This paper proposes OPMAC, a new medium access control (MAC) protocol designed for time-critical applications in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks (UWSNs). By establishing an on-demand data transmission pipeline and introducing a lightweight acknowledgment mechanism, OPMAC significantly reduces end-to-end delay and enhances energy efficiency, addressing the challenges of long propagation delays and high error rates in UWSNs.
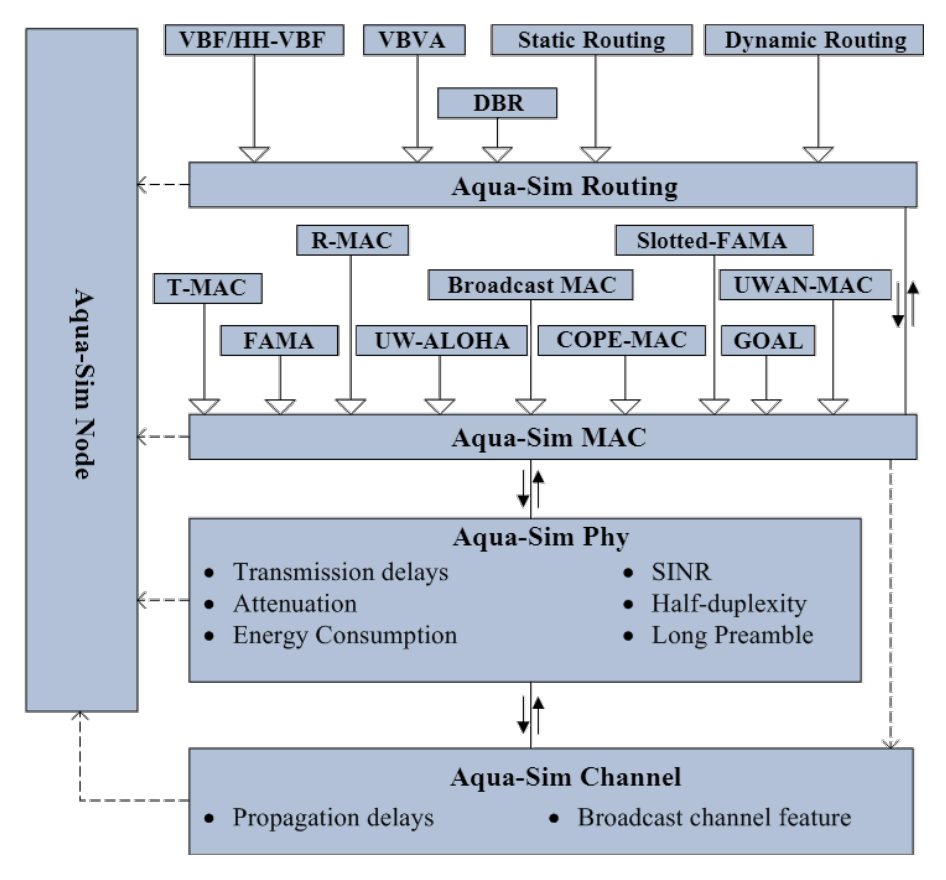
Aqua-Sim Next Generation: A NS-3 Based Simulator for Underwater Sensor Networks
Robert Martin, Yibo Zhu, Lina Pu, Fei Dou, Zheng Peng, Jun-Hong Cui, Sanguthevar Rajasekaran
Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems (WUWNet) 2015
This paper introduces Aqua-Sim: Next Generation, an improved underwater sensor network (UWSN) simulator built by transitioning Aqua-Sim 2.0 from NS-2 to NS-3 for better memory management and unified programming. The new version enhances performance, preserves existing protocol functionality, and adds features to more accurately model underwater environments and phenomena.
Aqua-Sim Next Generation: A NS-3 Based Simulator for Underwater Sensor Networks
Robert Martin, Yibo Zhu, Lina Pu, Fei Dou, Zheng Peng, Jun-Hong Cui, Sanguthevar Rajasekaran
Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems (WUWNet) 2015
This paper introduces Aqua-Sim: Next Generation, an improved underwater sensor network (UWSN) simulator built by transitioning Aqua-Sim 2.0 from NS-2 to NS-3 for better memory management and unified programming. The new version enhances performance, preserves existing protocol functionality, and adds features to more accurately model underwater environments and phenomena.
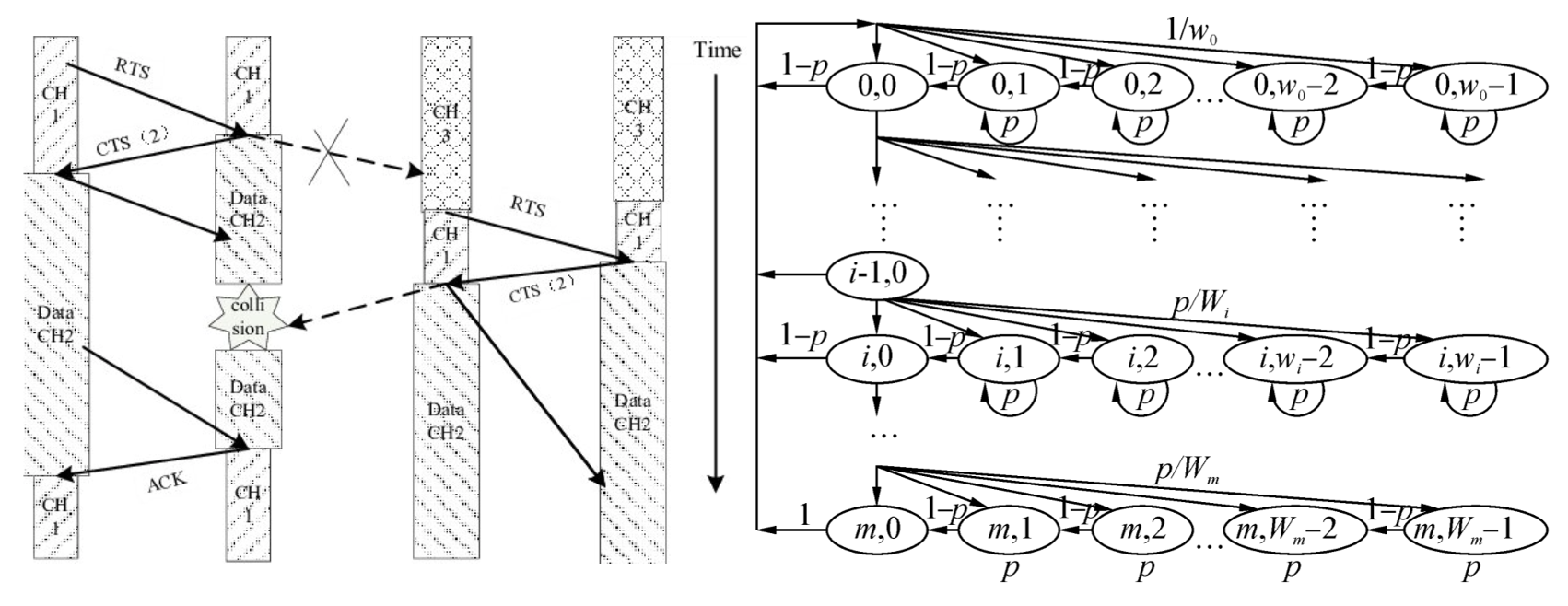
The Multi-Channel MAC Protocol for High Performance Underwater Sensor Networks
Yishan Su, Zhigang Jin, Fei Dou
Journal of Harbin Engineering University 36(7):987-991 2015
This paper introduces SFM-MAC, a multi-channel MAC protocol for underwater sensor networks that enhances spatial fairness and supports multi-channel communication using a single transducer. By incorporating location-aware RTS/CA/CL/CTS handshaking and a Markov-based reservation model, SFM-MAC improves fairness by 15% and achieves 60–70% and 12–15% higher throughput than slotted FAMA and UMMAC, respectively.
The Multi-Channel MAC Protocol for High Performance Underwater Sensor Networks
Yishan Su, Zhigang Jin, Fei Dou
Journal of Harbin Engineering University 36(7):987-991 2015
This paper introduces SFM-MAC, a multi-channel MAC protocol for underwater sensor networks that enhances spatial fairness and supports multi-channel communication using a single transducer. By incorporating location-aware RTS/CA/CL/CTS handshaking and a Markov-based reservation model, SFM-MAC improves fairness by 15% and achieves 60–70% and 12–15% higher throughput than slotted FAMA and UMMAC, respectively.
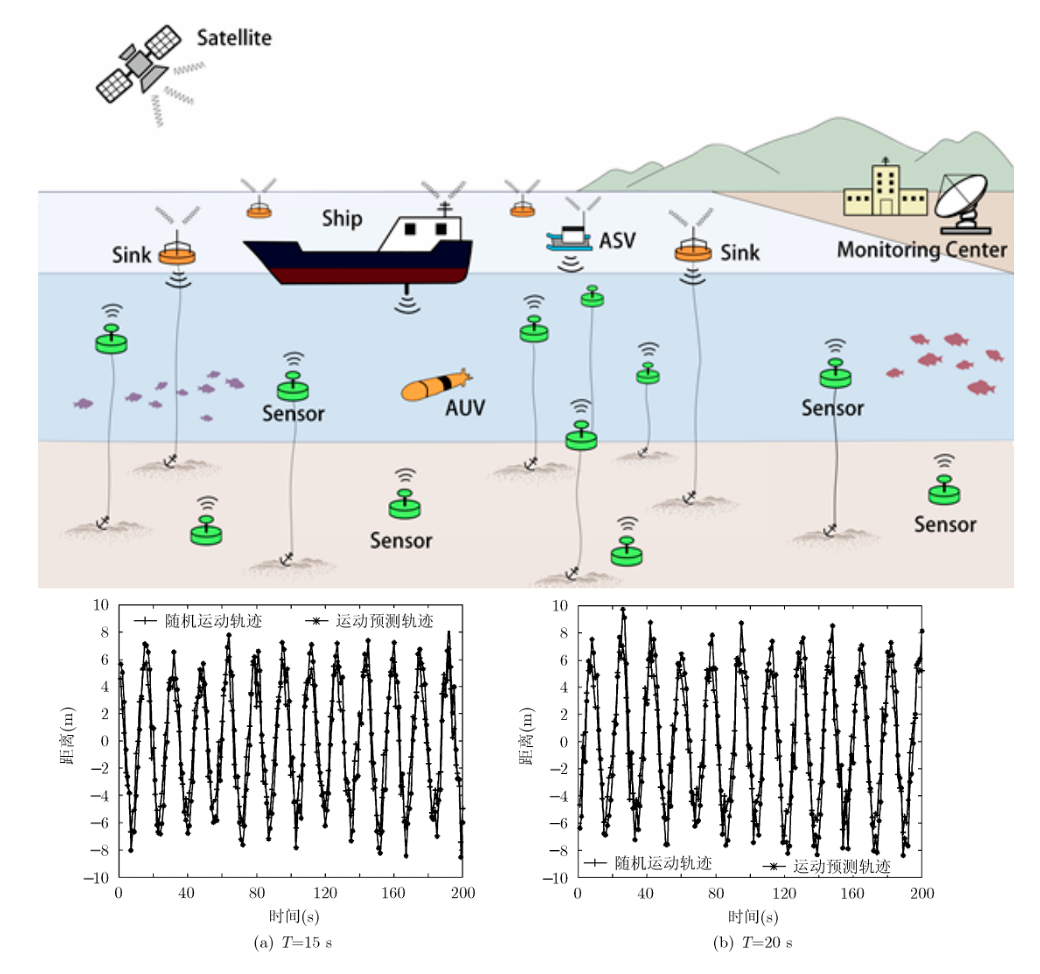
Motion Prediction Based MAC for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks
Zhigang Jin, Yishan Su, Zixin Liu, Fei Dou
Journal of Electronics & Information Technology 35(3):728-734 2013
This paper presents P-MAC, a contention-based MAC protocol designed for mobile Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks (UWSNs), addressing the challenges posed by node mobility and acoustic signal delays. By incorporating an autoregressive AR(5) mobility prediction algorithm to mitigate space-time uncertainty, P-MAC achieves up to 74.8% reduction in delay detection error and improves packet reception rate by 10–15% under wave-induced motion, as demonstrated in NS-2 simulations.
Motion Prediction Based MAC for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks
Zhigang Jin, Yishan Su, Zixin Liu, Fei Dou
Journal of Electronics & Information Technology 35(3):728-734 2013
This paper presents P-MAC, a contention-based MAC protocol designed for mobile Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks (UWSNs), addressing the challenges posed by node mobility and acoustic signal delays. By incorporating an autoregressive AR(5) mobility prediction algorithm to mitigate space-time uncertainty, P-MAC achieves up to 74.8% reduction in delay detection error and improves packet reception rate by 10–15% under wave-induced motion, as demonstrated in NS-2 simulations.