
 Assistant Professor (Tenure-Track)
Assistant Professor (Tenure-Track)School of Computing, the University of Georgia (UGA)
Fei Dou is an Assistant Professor in the School of Computing at the University of Georgia. She obtained her Ph.D. in 2023 from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at the University of Connecticut, where she worked in the Laboratory of Machine Learning & Health Informatics under the supervision of Prof. Jinbo Bi. Her work contributed to fundamental Machine Learning (ML) research for the Internet of Things (IoT) and Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), particularly in the areas of federated learning, reinforcement learning, and self-supervised learning.
Fei’s research focuses on advancing Machine Intelligence for Ubiquitous Computing in Distributed Systems, with an emphasis on scalable, responsible, and context-aware AI solutions.
Join Us: Our lab is seeking highly self-motivated PhD students to explore cutting-edge research in AI, machine learning and intelligent sensing.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 University of Connecticut (UConn)Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Ph.D.
University of Connecticut (UConn)Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Ph.D.
Supervisor: Dr. Jinbo BiSep 2018 - May 2023
Honors & Awards
-
Women of Innovation(WOI) Academic Innovation and Leadership, Connecticut2023
-
Provost Recognition of Teaching Excellence, University of Connecticut2017
News
Selected Publications (view all )
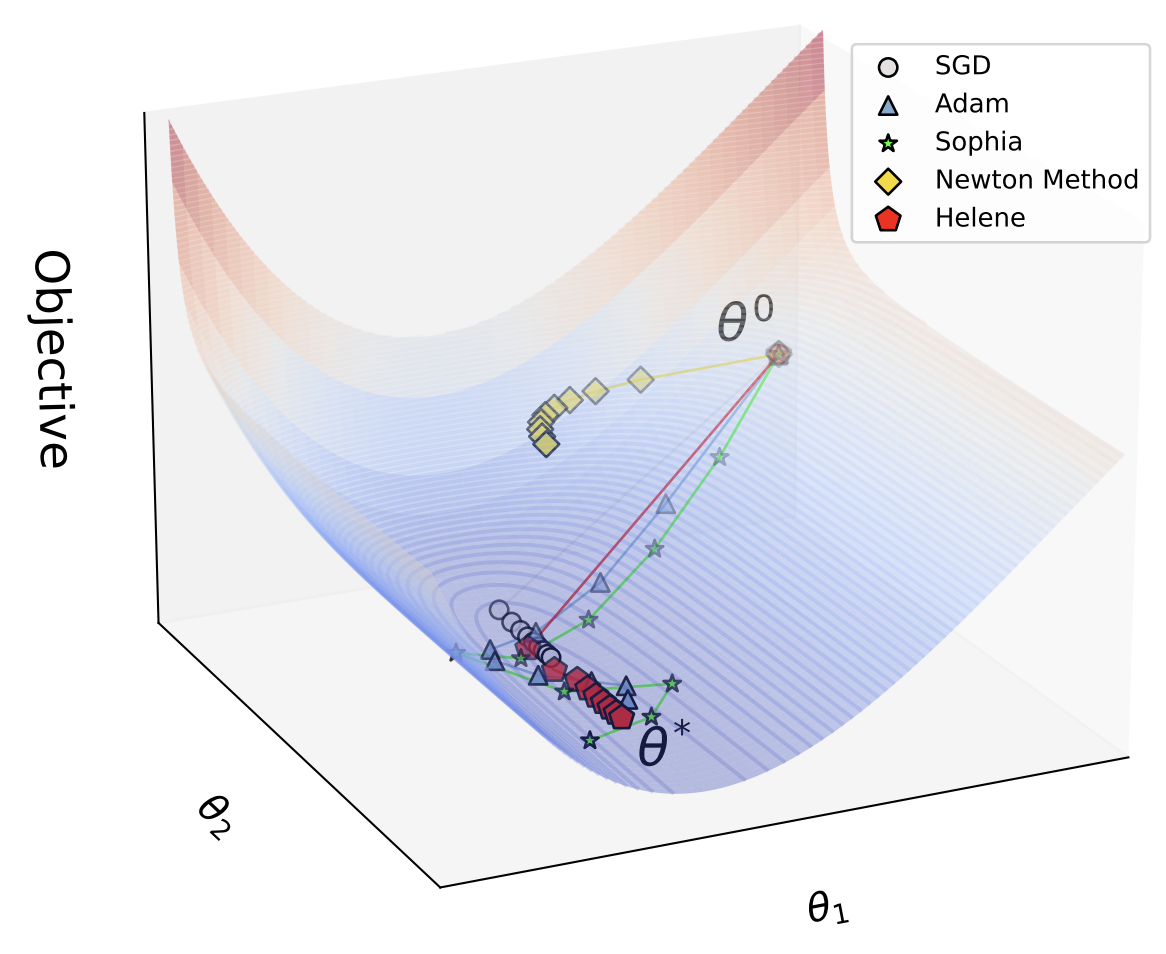
HELENE: Hessian Layer-wise Clipping and Gradient Annealing for Accelerating Fine-tuning LLM with Zeroth-order Optimization
Huaqin Zhao*, Jiaxi Li*, Yi Pan, Shizhe Liang, Xiaofeng Yang, Wei Liu, Xiang Li, Fei Dou, Tianming Liu, Jin Lu (* equal contribution)
Proceedings of the 2025 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025
This paper presents HELENE, a memory-efficient and scalable optimizer for fine-tuning large language models, addressing the slow convergence of zeroth-order methods like MeZO by incorporating annealed A-GNB gradients, diagonal Hessian estimation, and layer-wise clipping. HELENE achieves faster, more stable convergence with up to 20× speedup and improved accuracy, and it supports both full and parameter-efficient fine-tuning across large-scale models and tasks.
HELENE: Hessian Layer-wise Clipping and Gradient Annealing for Accelerating Fine-tuning LLM with Zeroth-order Optimization
Huaqin Zhao*, Jiaxi Li*, Yi Pan, Shizhe Liang, Xiaofeng Yang, Wei Liu, Xiang Li, Fei Dou, Tianming Liu, Jin Lu (* equal contribution)
Proceedings of the 2025 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2025
This paper presents HELENE, a memory-efficient and scalable optimizer for fine-tuning large language models, addressing the slow convergence of zeroth-order methods like MeZO by incorporating annealed A-GNB gradients, diagonal Hessian estimation, and layer-wise clipping. HELENE achieves faster, more stable convergence with up to 20× speedup and improved accuracy, and it supports both full and parameter-efficient fine-tuning across large-scale models and tasks.
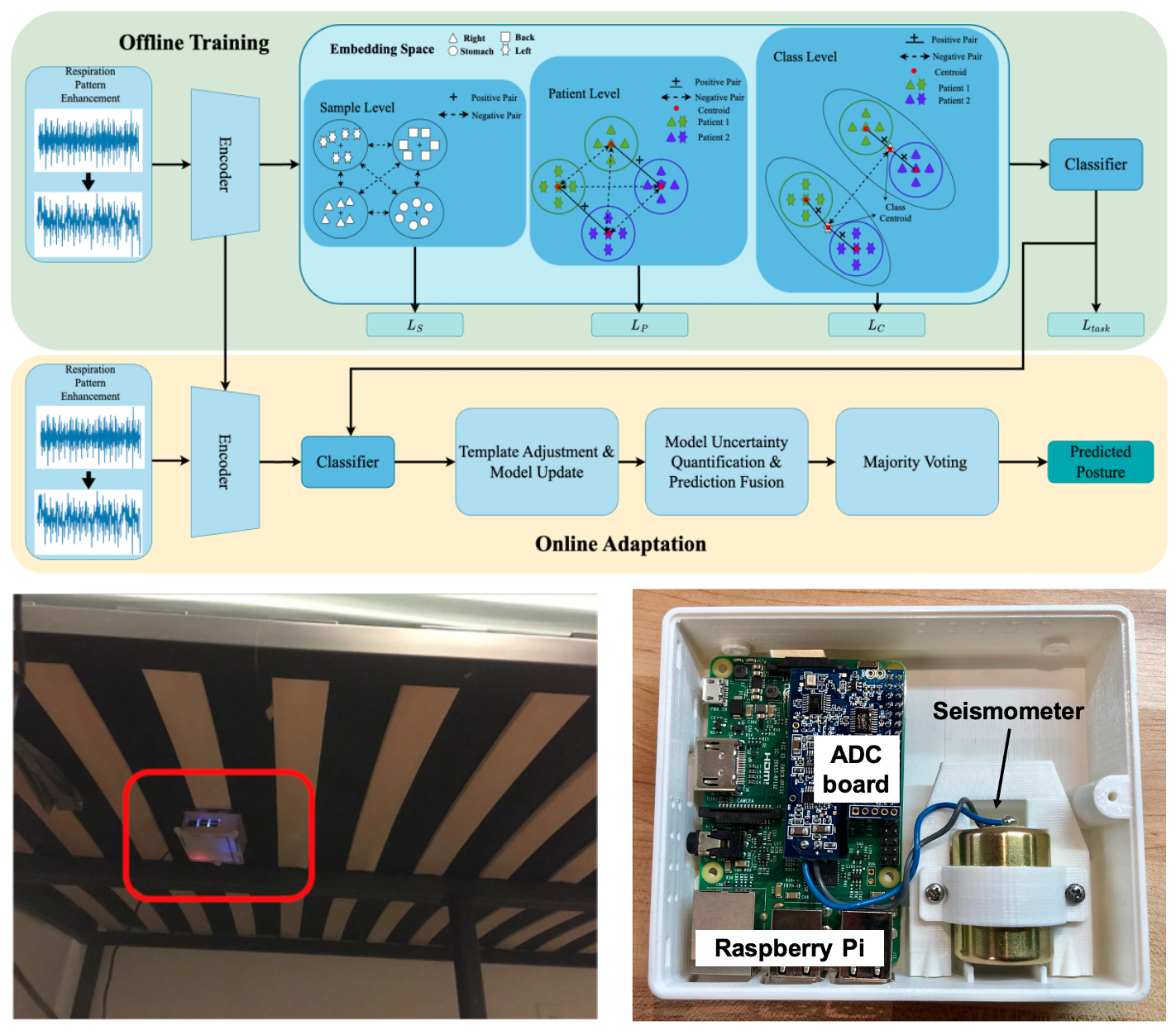
Multi-granularity Supervised Contrastive Learning with Online Adaptation for Contactless In-bed Posture Classification
Yingjian Song, Haotian Xiang, Zixuan Zeng, Jiayu Chen, Yida Zhang, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, He Yang, Qin Lu, Xiang Zhang, Bradley G Phillips, Fei Dou, WenZhan Song
Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (UbiComp/IMWUT) 2025
This paper presents a privacy-friendly, easy-to-deploy in-bed posture classification framework using seismic sensors, integrating a Multi-Granularity Supervised Contrastive Learning (MGSCL) module and an ensemble Online Adaptation (OA) module. The system effectively adapts to individual variations and unlabeled data, achieving high accuracy (91.67%) and F1 score (91.53%) with minimal labeled data in clinical settings, and maintaining strong performance in home environments, highlighting its potential for sleep quality and health monitoring.
Multi-granularity Supervised Contrastive Learning with Online Adaptation for Contactless In-bed Posture Classification
Yingjian Song, Haotian Xiang, Zixuan Zeng, Jiayu Chen, Yida Zhang, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, He Yang, Qin Lu, Xiang Zhang, Bradley G Phillips, Fei Dou, WenZhan Song
Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (UbiComp/IMWUT) 2025
This paper presents a privacy-friendly, easy-to-deploy in-bed posture classification framework using seismic sensors, integrating a Multi-Granularity Supervised Contrastive Learning (MGSCL) module and an ensemble Online Adaptation (OA) module. The system effectively adapts to individual variations and unlabeled data, achieving high accuracy (91.67%) and F1 score (91.53%) with minimal labeled data in clinical settings, and maintaining strong performance in home environments, highlighting its potential for sleep quality and health monitoring.
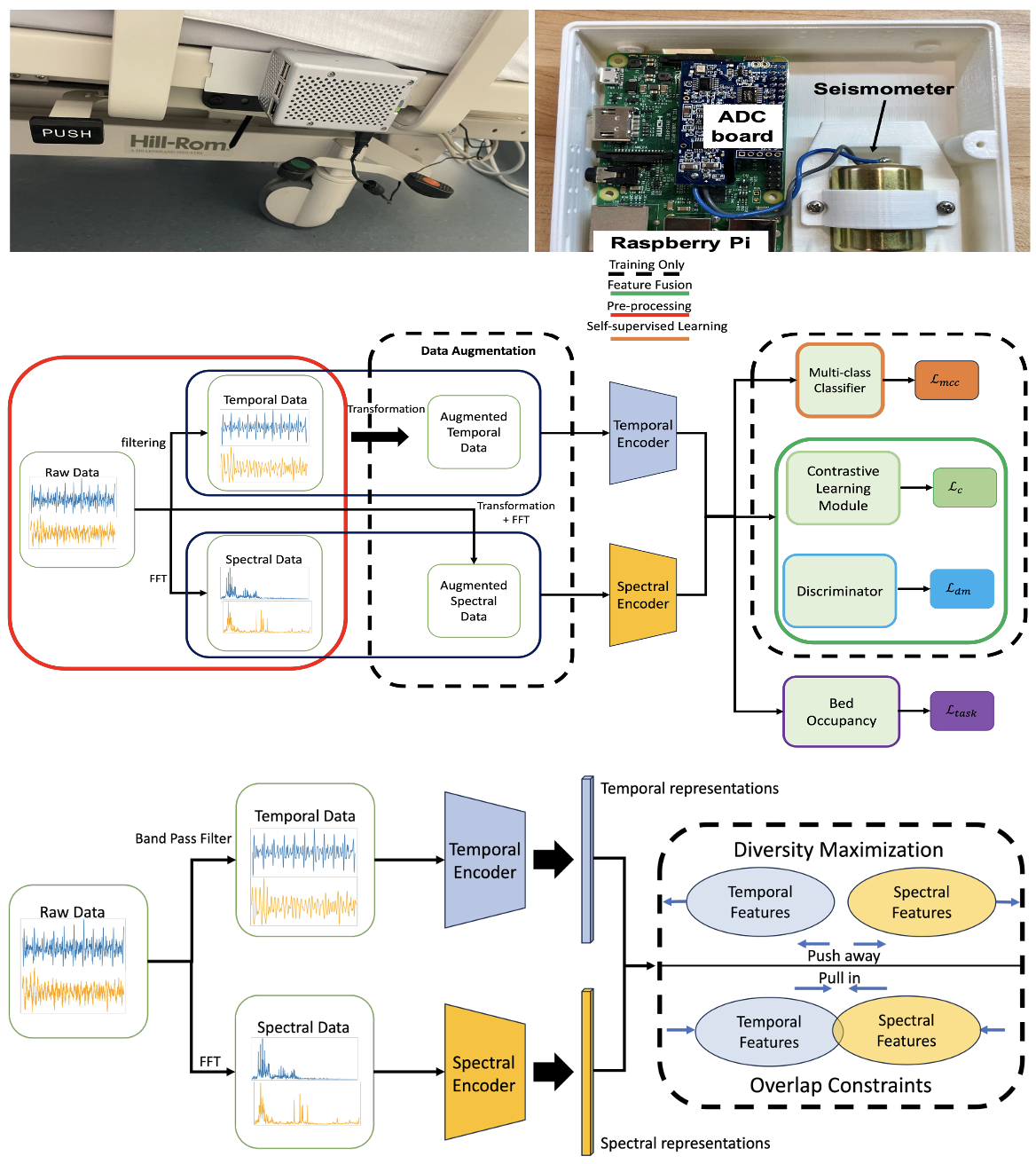
Self-Supervised Representation Learning and Temporal-Spectral Feature Fusion for Bed Occupancy Detection
Yingjian Song, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, Fei Dou, Jin Sun, Xiang Zhang, Bradley G Phillips, WenZhan Song
Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (UbiComp/IMWUT) 2024
This paper presents SeismoDot, a bed occupancy detection system that combines self-supervised learning and spectral-temporal feature fusion to improve generalization across diverse environments with limited data. Unlike traditional threshold-based methods, SeismoDot achieves high accuracy and F1 scores across 13 settings and remains effective even when trained on only 20% of the data, demonstrating strong adaptability and efficiency.
Self-Supervised Representation Learning and Temporal-Spectral Feature Fusion for Bed Occupancy Detection
Yingjian Song, Zaid Farooq Pitafi, Fei Dou, Jin Sun, Xiang Zhang, Bradley G Phillips, WenZhan Song
Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (UbiComp/IMWUT) 2024
This paper presents SeismoDot, a bed occupancy detection system that combines self-supervised learning and spectral-temporal feature fusion to improve generalization across diverse environments with limited data. Unlike traditional threshold-based methods, SeismoDot achieves high accuracy and F1 scores across 13 settings and remains effective even when trained on only 20% of the data, demonstrating strong adaptability and efficiency.
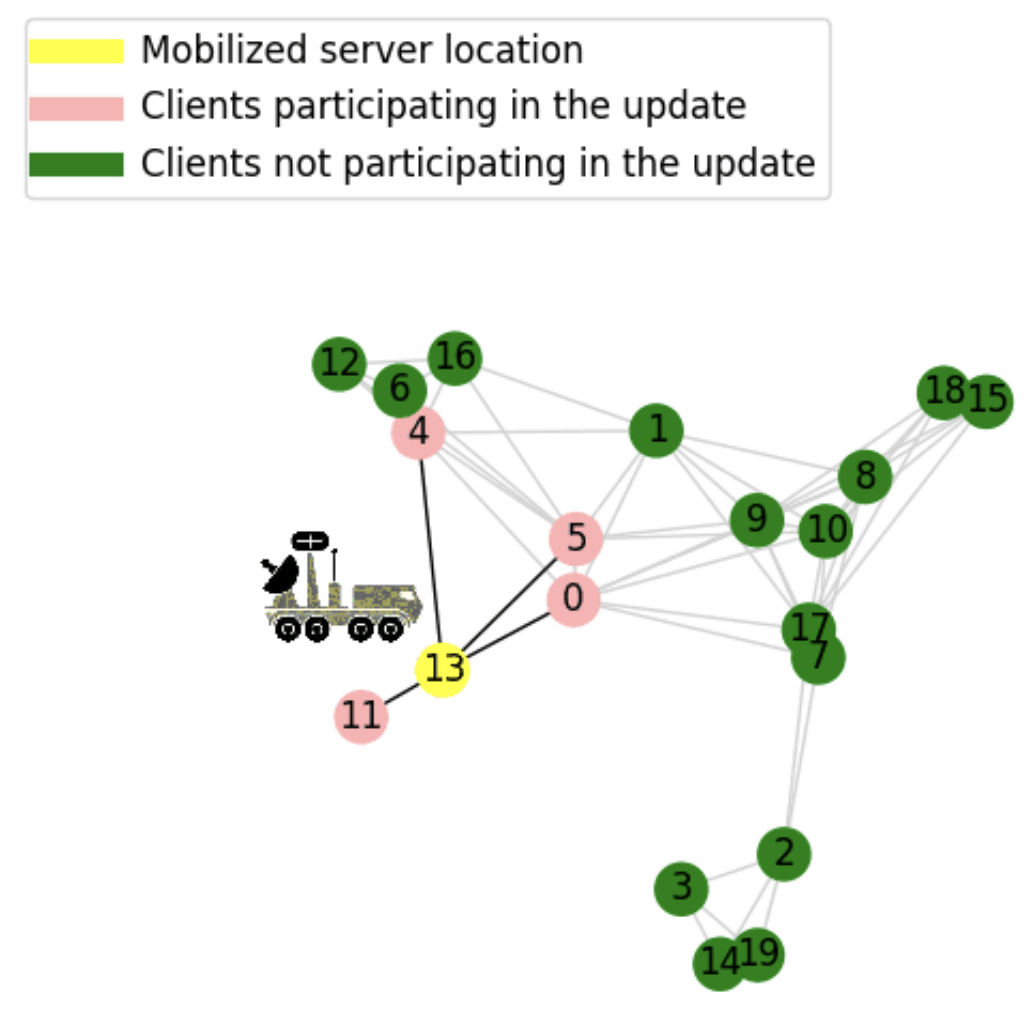
Mobilizing Personalized Federated Learning in Infrastructure-Less and Heterogeneous Environments via Random Walk Stochastic ADMM
Ziba Parsons, Fei Dou, Houyi Du, Zheng Song, Jin Lu
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 (NeurIPS) 2023
This paper proposes RWSADMM, a novel federated learning algorithm designed for infrastructure-less environments with isolated, heterogeneous nodes connected via wireless links. By leveraging server mobility and enforcing hard constraints among adjacent clients, RWSADMM enables efficient, personalized learning with provable convergence, reduced communication costs, and improved accuracy and scalability over baseline methods.
Mobilizing Personalized Federated Learning in Infrastructure-Less and Heterogeneous Environments via Random Walk Stochastic ADMM
Ziba Parsons, Fei Dou, Houyi Du, Zheng Song, Jin Lu
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 (NeurIPS) 2023
This paper proposes RWSADMM, a novel federated learning algorithm designed for infrastructure-less environments with isolated, heterogeneous nodes connected via wireless links. By leveraging server mobility and enforcing hard constraints among adjacent clients, RWSADMM enables efficient, personalized learning with provable convergence, reduced communication costs, and improved accuracy and scalability over baseline methods.
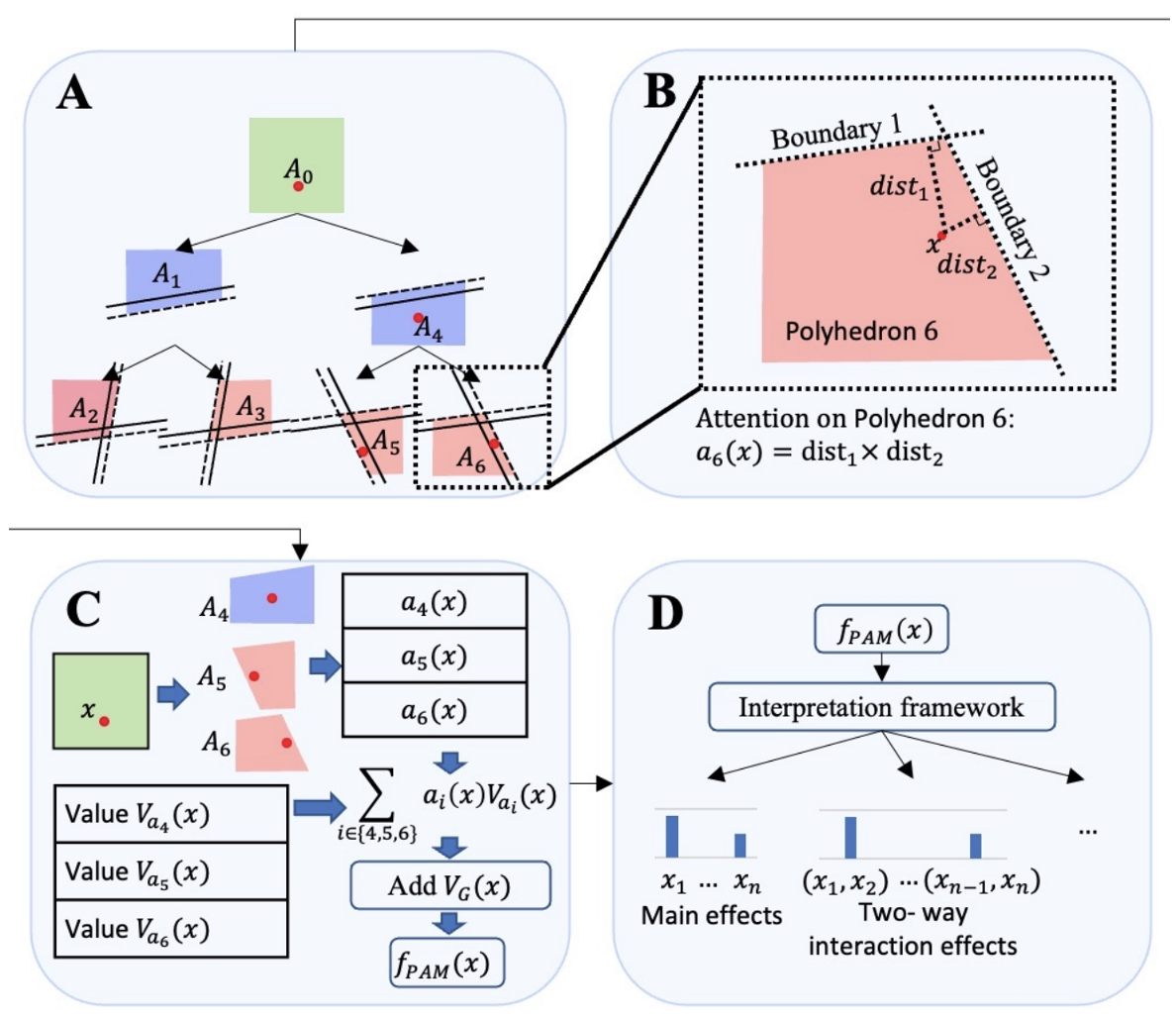
Polyhedron Attention Module: Learning Adaptive-order Interactions
Tan Zhu, Fei Dou, Xinyu Wang, Jin Lu, Jinbo Bi
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 (NeurIPS) 2023
This paper introduces the Polyhedron Attention Module (PAM), which forms interpretable, piecewise polynomial models by adaptively learning feature interactions within polyhedrons in the input space. PAM outperforms ReLU-based networks in expressive power and achieves superior classification results on large-scale click-through rate datasets while uncovering meaningful interactions in medical applications.
Polyhedron Attention Module: Learning Adaptive-order Interactions
Tan Zhu, Fei Dou, Xinyu Wang, Jin Lu, Jinbo Bi
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 36 (NeurIPS) 2023
This paper introduces the Polyhedron Attention Module (PAM), which forms interpretable, piecewise polynomial models by adaptively learning feature interactions within polyhedrons in the input space. PAM outperforms ReLU-based networks in expressive power and achieves superior classification results on large-scale click-through rate datasets while uncovering meaningful interactions in medical applications.
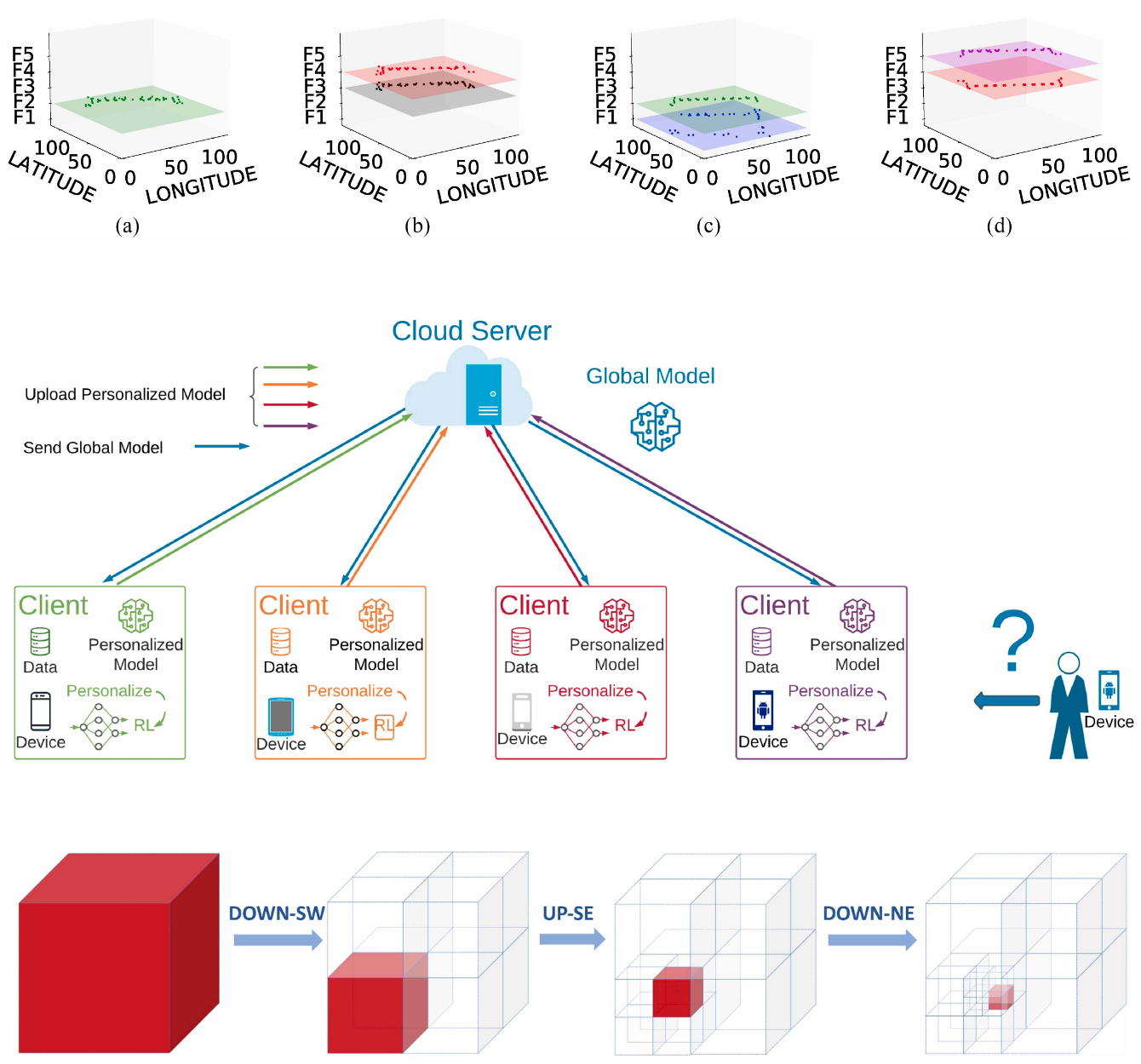
On-Device Indoor Positioning: A Federated Reinforcement Learning Approach With Heterogeneous Devices
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Tan Zhu, Jinbo Bi
IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IOT-J) 2023
This paper proposes a personalized federated reinforcement learning (RL) framework for indoor localization that enables mobile devices to train locally while preserving data privacy and coping with limited connectivity and data heterogeneity. By combining personalized on-device RL with a global model trained via sparse updates, the approach achieves improved localization accuracy and robustness, and is further extended to support few-shot learning for rapid adaptation to new users with minimal data.
On-Device Indoor Positioning: A Federated Reinforcement Learning Approach With Heterogeneous Devices
Fei Dou, Jin Lu, Tan Zhu, Jinbo Bi
IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IOT-J) 2023
This paper proposes a personalized federated reinforcement learning (RL) framework for indoor localization that enables mobile devices to train locally while preserving data privacy and coping with limited connectivity and data heterogeneity. By combining personalized on-device RL with a global model trained via sparse updates, the approach achieves improved localization accuracy and robustness, and is further extended to support few-shot learning for rapid adaptation to new users with minimal data.
All publications
Visitor Map